Fig. 7.
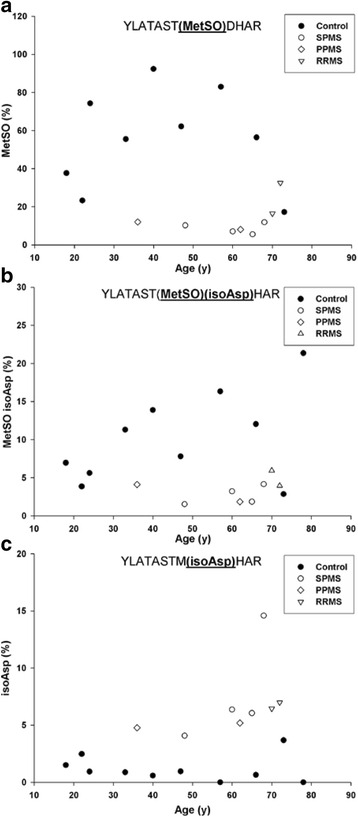
Oxidation of Met22 coupled with racemization of Asp23 in MBP from controls (●) and multiple sclerosis (MS) patients suffering from SPMS (○) PPMS (◊) and RRMS (▽). a When all Asp versions of (YLATASTMDHAR) were included, Met oxidation in the controls was significantly greater than in multiple sclerosis patients (p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney-U). b Oxidation of Met22 and racemization of Asp23 to isoAsp in YLATASTMDHAR. In the Met-oxidized peptide, racemization of Asp23 (YLATAST(MetSO)(isoAsp)HAR) was greater in the control samples (p = 0.008, Mann–Whitney-U). IsoAsp in this case refers to combined D- and L-isoAsp, since the isomers were not separated under these conditions. c Racemization of Asp23 to isoAsp(YLATASTM(isoAsp)HAR) in the absence of Met oxidation. Levels of isoAsp were significantly higher in multiple sclerosis patients (p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney-U). The percentage of modification was determined by the ion intensities of (Modified YLATASTMDHAR)/(YLATASTMDHAR + YLATASTMDHAR) × 100. Controls n = 10; multiple sclerosis patients n = 8
