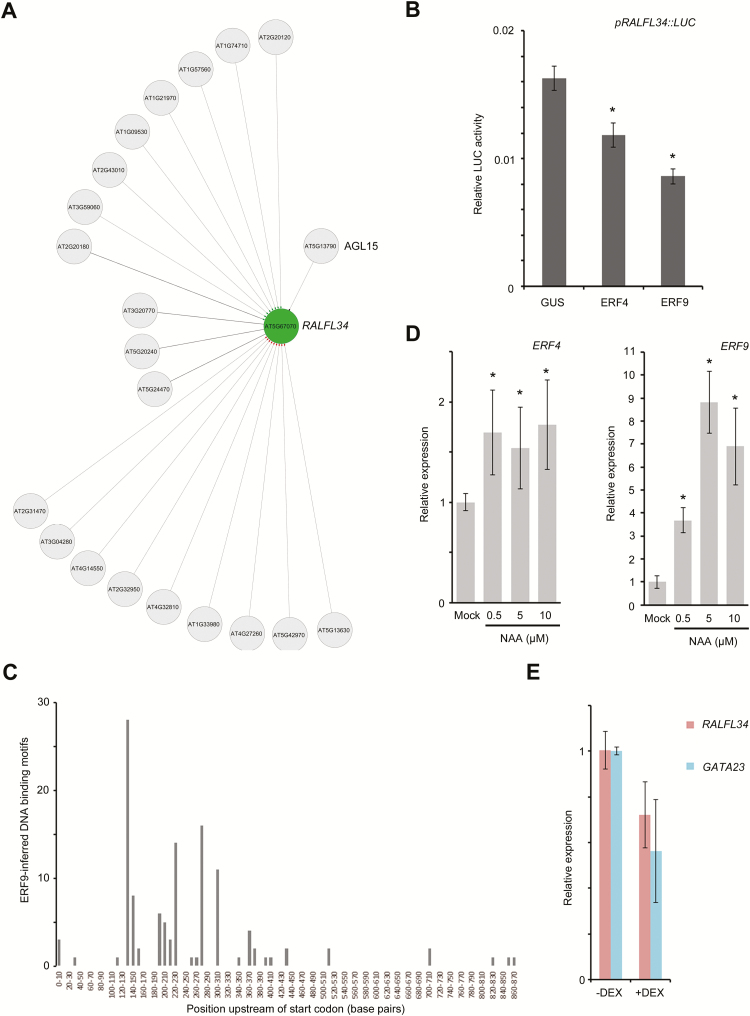
Fig. 6.
ERFs regulated RALFL34 expression. (A) In silico generated transcription factor network, highlighting putatively interacting proteins with RALFL34 in CORNET. Interactions are as follows: confirmed (full line), unconfirmed (dotted line), indirect (diamond), direct+unknown (disc), direct+activation (arrowhead), direct+repression [line activation (green), repression (red), and unknown (black)]. (B) Luciferase (LUC) activity upon co-expression of pRALFL34::LUC and GUS (control) or ERF4/9 in protoplasts. Luciferase assay was performed three times, each time with eight biological replicates. The graph shows the average of all 24 data points ±SE. Student’s t-test with P-value <0.01. (C) Number of ERF9-inferred DNA-binding motifs according to their position upstream of the coding sequence (start codon=position 0). (D) ERF4 and ERF9 expression upon 6h of NAA treatment at the indicated concentrations. The graph shows the average ±SE error of three biological repeats. *P<0.05 according to Student’s t-test compared with mock. (E) Expression of RALFL34 and GATA23 in an inducible ERF9 overexpression line (35S::ERF9-GR) after 4h of DEX-induced overexpression of ERF9.