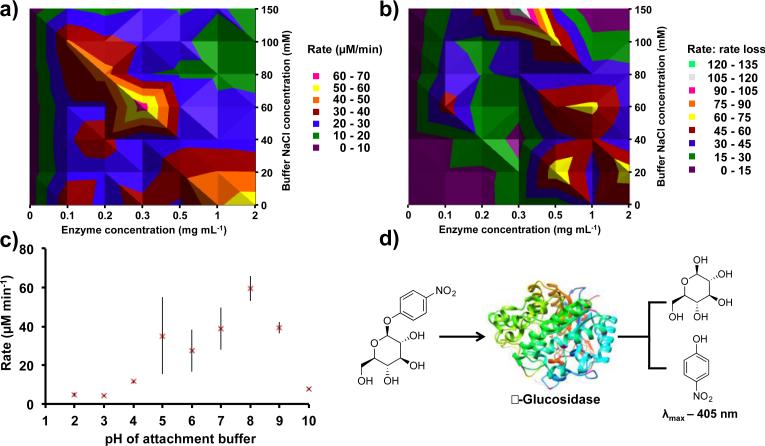
Fig. 2. Non-covalent immobilization using β-glucosidase and 4-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside for optimization.
(a) The enzyme and buffer salt concentration were varied during the immobilization step. The contour plot reveals that a 0.3 mg mL enzyme concentration in a 60 mM NaCl PBS buffer is optimal for high substrate conversion. (b) Decreased catalytic activity due to enzyme leaching is depicted in this contour plot. Thus, higher salt concentrations are revealed as beneficial for immobilization longevity. (c) Varying the pH of the attachment buffer established optimal immobilization in PBS at pH 8.0. The deviation from the trend at pH 5.0 is due to the isoelectric point of β-glucosidase. (d) For all optimization experiments, a β-glucosidase - 4-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside (10 mM, 1.50 mL) system was used. β-glucosidase hydrolyses the substrate, releasing p-nitrophenol (λmax 405 nm) and β-D-glucopyranoside. Each assay was performed in the VFD for five min, and each reactor was assayed six times. Two separate reactors were used per data point, and the error is a standard deviation around the mean (n=12).