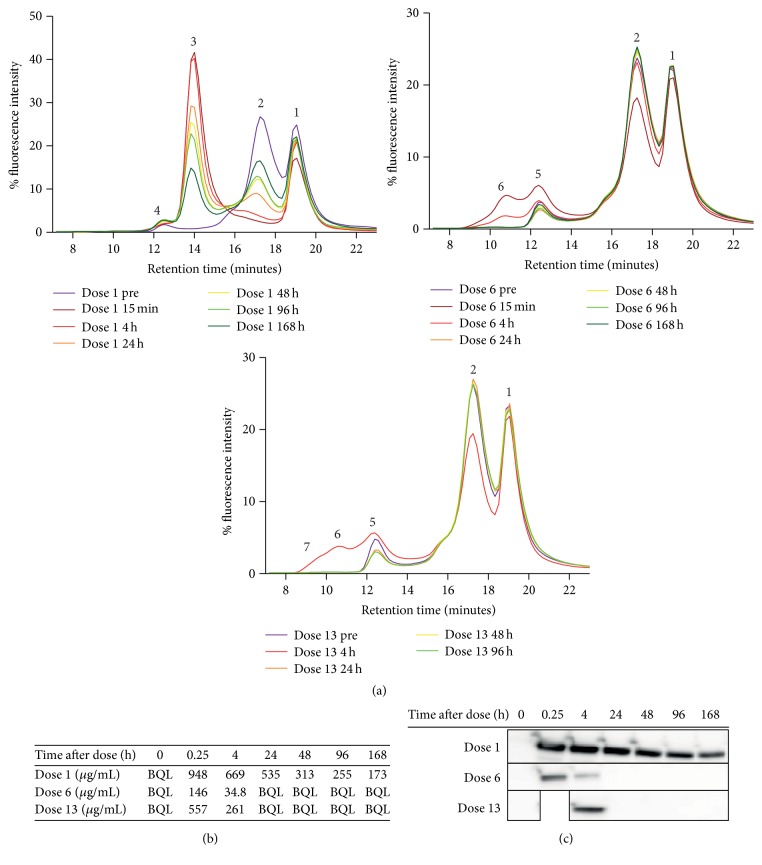
Figure 4.
(a) SEC profile of toxicology study animal. 678 nM Fab488 was incubated with 20% serum samples from a cynotoxicology study with huDVD as described in Section 2 and separated by size exclusion chromatography with fluorescence detection. Peak 1 is the free dye (DyLight 488), peak 2 is Fab488, peak 3 is the complex of Fab488 and huDVD, peak 4 is unspecific binding, peak 5 is the complex of Fab488 and huDVD and one ADA, peak 6 is the complex of Fab488, huDVD, and two ADAs, and peaks under number 7 represent bigger complexes containing Fab488, huDVD, and ADA. Graph 1 shows the chromatographic traces of the predose sample (dose 1 pre) of one animal before the first dose and 15 minutes, 4 hours, 24 hours, 48 hours, 96 hours, and 168 hours after the first dose (from dark purple to dark green, dose 1 15 min–dose 1 168 h). Graph 2 shows chromatogram traces of the predose sample (dose 6 pre) of the same animal before dose 6 and 15 minutes, 4 hours, 24 hours, 48 hours, 96 hours, and 168 hours after the 6th dose (from dark purple to dark green, dose 6 15 min–dose 6 168 h). Graph 3 shows the chromatographic traces of the predose sample (dose 13 pre) of the same animal before dose 13 and 4 hours, 24 hours, 48 hours, and 96 hours after the 13th dose (from dark purple to green, dose 13 15 min–dose 13 96 h). The 15 minutes and 168 hours postdose samples were missing here. (b) PK profile of the same study animal measured with ligand binding assay. The concentration in μg/mL of huDVD was measured with an antigen-based ligand binding assay using Mesoscale Discovery ECL technology. The figure depicts the concentration in 100% serum in the predose and postdose samples of doses 1, 6, and 13 for the same animal as in (a). BQL indicates that the values were below the lower limit of quantitation. (c) Relative quantitation of total amounts of huDVD with western blot. The same study samples as in (a) and (b) were separated by nonreducing SDS-PAGE and analyzed with western blot as described in Section 2. The huDVD signal is shown.