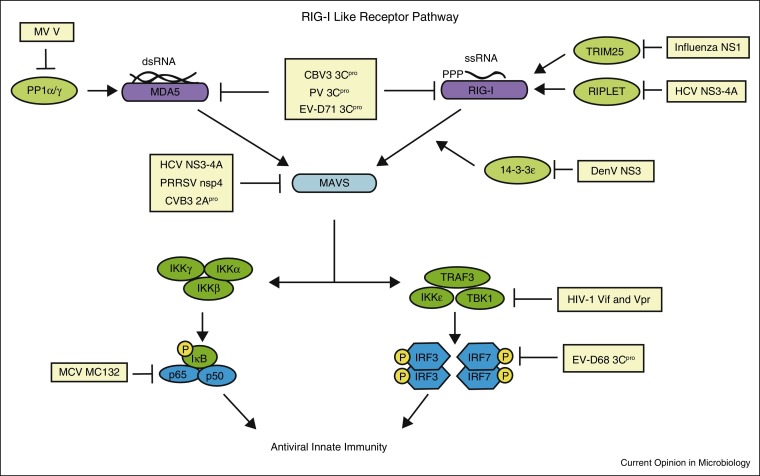
Figure 1.
Evasion of RIG-I-like receptor signaling by viruses. The RIG-I-like receptors RIG-I and MDA5 are activated by viral dsRNA in the cell cytoplasm. PP1α/γ dephosphorylates MDA5 to allow subsequent signaling. TRIM25 and RIPLET are E3 ubiquitin ligases that ubiquitinate RIG-I for its full activation. The 14-3-3ɛ protein mediates RIG-I translocation to the membrane to interact with MAVS. MAVS is the adaptor protein for both RIG-I and MDA5 and recruits downstream signaling molecules to mediate signaling to the transcription factors IRF3/7 and NFκB. Several aspects of this signaling pathway are inhibited by viruses, as shown here. Abbreviations: coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3), dengue virus (DenV), enterovirus 68 (EV-D68), enterovirus 71 (EV-D71), hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), poliovirus (PV), porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), and West Nile virus (WNV).