Fig. (1).
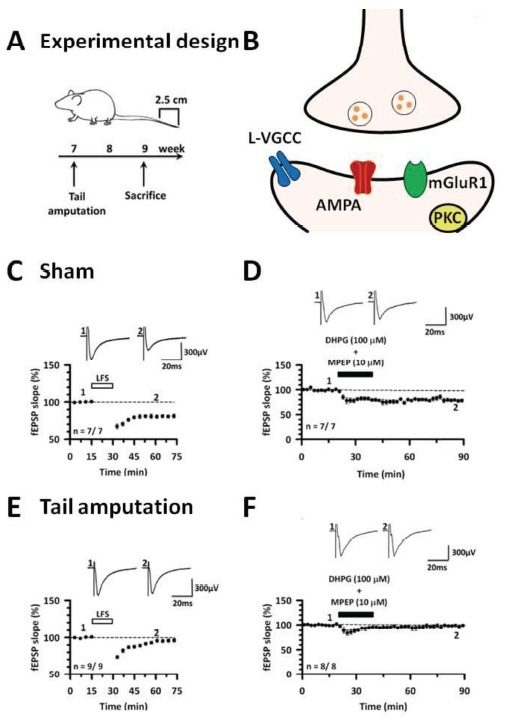
The cingulate LTD and occlusion by tail amputation. (A) Experimental design of cingulate LTD and tail amputation. (B) The mechanisms of cingulate LTD using fEPSP recording. (C) Low-frequency stimulation (1 Hz for 15 min) produces LTD in the ACC. (D) The activation of mGluR1 by a group I mGluR agonist DHPG (100 μM) together with a mGluR5 antagonist MPEP (10 μM) show cingulate LTD in sham mice. (E) The 2 weeks of tail amputation model mice show impaired cingulate LTD. (F) Twenty minute after DHPG with MPEP show no chemical induced LTD in the ACC of the amputation model mice. Modified from [22].
