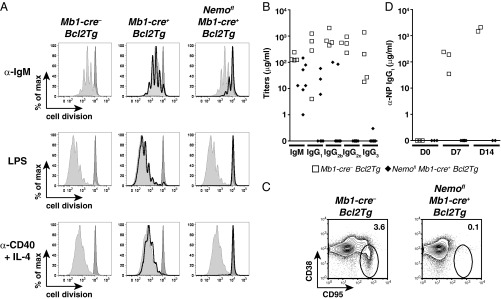
Fig. 2.
Mature B cells from Nemofl Mb1-cre+ Bcl2Tg mice are functionally defective. (A) Proliferation of live splenic mature B cells from Mb1-cre− Bcl2Tg (light gray-filled histogram), Mb1-cre+ Bcl2Tg (black histogram), and Nemofl Mb1-cre+ Bcl2Tg (black histogram) mice that were MACS-purified; labeled with cell proliferation dye eFluor 450; and stimulated with 10 μg/mL anti-IgM (α-IgM), 20 μg/mL LPS, or 1 μg/mL anti-CD40 + 25 ng/mL IL-4 (α-CD40 + IL-4) for 4 d. The dark gray-filled histogram shows resting Mb1-cre− Bcl2Tg B cells. At least three mice per genotype were analyzed in independent experiments. max, maximum. (B) Serum Ab isotype titers in sera of naive mice (n = 4–7 per genotype). (C) Flow cytometry of CD38loCD95+ germinal center B cells within splenic B220+ cells of mutant and control mice 14 d after immunization with NP-CGG. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas specify the percentage of cells in each gate. Five mice were analyzed per genotype in two experiments. (D) Serum titers of NP-specific IgG1 (n = 2–6 per group). D0, unimmunized mice; D7 and D14, day 7 and day 14 postimmunization. One control mouse at D7 did not respond to the immunization and was excluded from the analysis. Data are representative of two experiments. In B and D, symbols indicate individual mice.