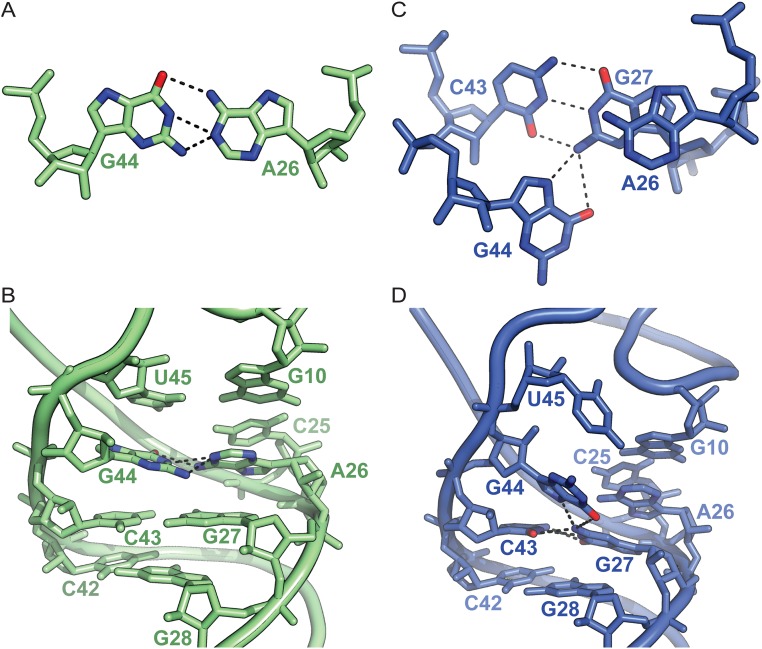
Fig. S7.
Structural plasticity in the core of the tRNA body. (A) Top view of the G44-A26 imino base pair observed in the A-site tRNAPhe from a previous 70S ribosome structure [PDB ID code 4V51 (45)]. (B) Side view of the junction between the anticodon/D helical domains in the same ribosome-bound tRNAPhe. (C) Top view of the same region within the A/L-tRNA. The EF-4–induced remodeling of the A/L-tRNA is facilitated by nucleotide rearrangements in the core of the tRNA body. Nucleotide G44 bulges out of the anticodon/D helical domains and forms a new base triple with base pair G27–C43. (D) Side view of the A/L-tRNA showing the distortion of the continuous stacking between the anticodon/D helical stems. Putative hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashes.