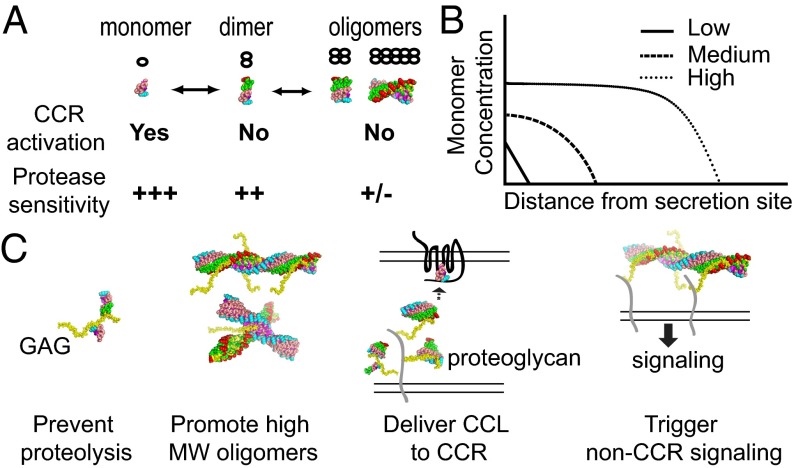
Fig. 6.
Roles of oligomerization, GAG binding, and proteolytic degradation of CC chemokines. (A) Equilibrium of CC chemokine oligomeric states and their properties in receptor binding and protease sensitivity. (B) Distribution of monomeric CC chemokine (log scale) from the source over the distance (linear scale). At low and medium levels of CC chemokine where it is most monomer or a mixture of monomer and dimer, respectively, cells will be directed to the center of CC chemokine source. However, at high CC chemokine level where it also forms oligomer, cells will only be migrated to the peripheral of CC chemokine source, rather than to the center. This would help to prevent the spread of invading pathogens in a severe infection. This is because the difference in CC chemokine monomer level within the cell length is less than required difference for the effective chemotaxis. (C) Effects of GAG binding and oligomerization to the functions of CC chemokines (see Discussion).