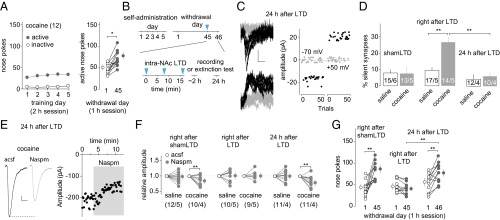
Fig. 1.
Transient anti-incubation effects of BLA-to-NAc LTD. (A) Summarized results showing that, after 5 d of cocaine self-administration (2 h/d at 0.75 mg/kg) following an overnight training, cue-induced cocaine seeking (measured by nose pokes in a 1-h extinction) was increased 45 d after withdrawal from cocaine compared with withdrawal day 1 [t(11) = 4.87; P < 0.01, paired t test; the same rats tested on withdrawal days 1 and 45]. (B) Time line of behavioral procedure showing that in vivo LTD induction (blue arrows, 5 Hz × 3 min × 3 times with 5-min intervals) was applied to BLA-to-NAc synapses 45 d after saline or cocaine self-administration. Electrophysiology or extinction tests were performed either right after or 24 h after BLA-to-NAc LTD. (C) Example EPSCs evoked at −70 or +50 mV from BLA-to-NAc synapses by optogenetic minimal stimulations (Left) over 100 trials (Right) 24 h after in vivo LTD in rats after 45 d of cocaine withdrawal. (D) Summarized results showing that, similar to previous results (16), on withdrawal day 45, whereas the percentage of silent synapses in BLA-to-NAc projection in cocaine-exposed rats returned to basal (saline) levels, this percentage was significantly increased upon LTD induction (LTD: saline, 9.5 ± 1.8; cocaine, 26.3 ± 2.9; shamLTD: saline, 8.1 ± 2.0; cocaine, 8.1 ± 5.1, measured right after LTD/shamLTD), and this LTD effect on the percentage of silent synapses diminished after 24 h [saline, 4.3 ± 3.1; cocaine, 6.2 ± 1.9; F(2,23) = 4.7, P < 0.05, two-way ANOVA; P < 0.01, right after LTD vs. 24 h after LTD in cocaine groups; P < 0.01, saline right after LTD vs. cocaine right after LTD; Bonferroni posttest]. n/m, n cells from m rats. (E) Example EPSCs (Left) and the time course (Right) of BLA-to-NAc synapses before and during perfusion of Naspm in a cocaine-exposed rat 24 h after the withdrawal day 45 LTD. (F) Summarized results showing that on withdrawal day 45, in vivo LTD, but not shamLTD, abolished the cocaine withdrawal-induced increase in the sensitivity of EPSCs at BLA-to-NAc synapses to Naspm when tested right after LTD induction. This LTD effect diminished after 24 h. Evoked EPSCs at BLA-to-NAc synapses in saline-exposed rats were insensitive to Naspm right after shamLTD, right after LTD, or 24 h after LTD [F(5,21) = 4.2, P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures; P < 0.01, before vs. during Naspm in cocaine rats right after shamLTD; P < 0.01, before vs. during Naspm in cocaine rats 24 h after LTD]. (G) Summarized results showing that incubation of cocaine craving (increased number of nose pokes for cocaine on withdrawal day 45 or 46 compared with withdrawal day 1) was not affected right after shamLTD to BLA-to-NAc synapses and was abolished right after LTD, but this LTD effect diminished after 24 h [F(2,30) = 10.9, P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures; P < 0.01, withdrawal day 1 vs. day 45 in rats right after shamLTD or 24 h after LTD, Bonferroni posttest]. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.