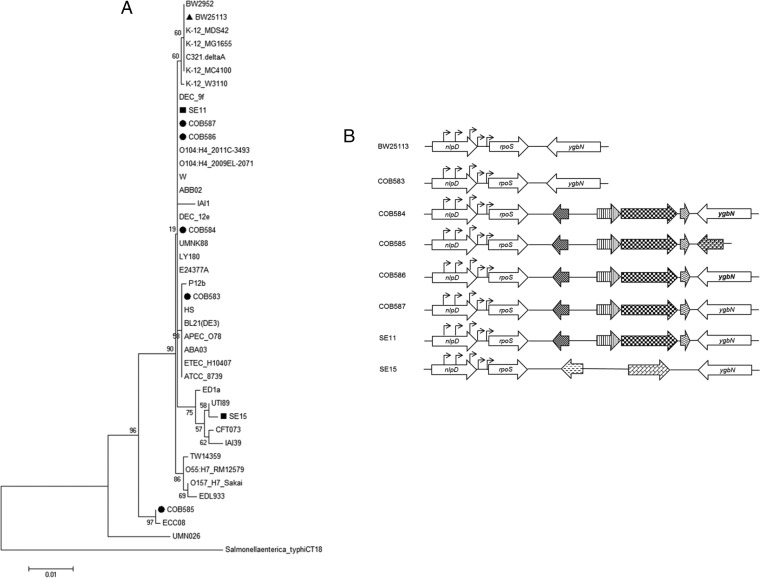
FIG 3.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of rpoS performed using the maximum likelihood method based on the Kimura 2-parameter model with bootstrap analysis (1,000 iterations) using MEGA6 showed that rpoS in soil-persistent strains is similar to previously known E. coli strains. (B) Gene outline of rpoS and its flanking genes in the soil-persistent and commensal strains shows four distinct patterns. PCR and sequencing of genes flanking rpoS revealed insertion of open reading frames (ORFs) between rpoS and inner membrane permease (ygbN). Pattern I (COB583), which is similar to the reference strain (BW25113), shows rpoS directly flanked by murein hydrolase activator (nlpD) and ygbN. Pattern II (COB584, COB586, COB587, and SE11) shows insertion of 4 ORFs between rpoS and ygbN. Pattern III (COB585) shows insertion of 5 ORFs after rpoS, with ygbN absent, while pattern IV (SE15) had insertion of 2 ORFs between rpoS and ygbN. The region between nlpD (which carried rpoS promoters) and rpoS was conserved in all the strains. Block arrows with similar patterns indicate the same ORF, while arrowheads represent rpoS promoter sites.