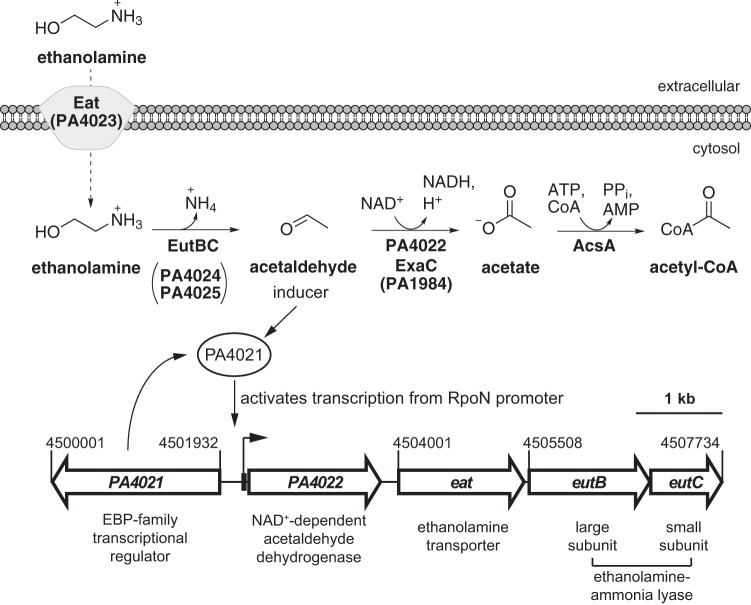
FIG 1.
Proposed catabolic pathway for ethanolamine in P. aeruginosa PAO1. The PA4022-eat-eutBC operon encodes a central catabolic pathway for ethanolamine. Ethanolamine enters the bacterium through simple diffusion and/or transport mediated by Eat (PA4023). Intracellular ethanolamine is hydrolyzed into ammonia and acetaldehyde by ethanolamine-ammonia lyase, which is composed of large EutB (PA4024) and small EutC (PA4025) subunits. The acetaldehyde intermediate is converted into acetate via an NAD+-dependent acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, PA4022 and/or ExaC (PA1984). Acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) synthetase (AcsA) is required for acetate utilization in P. aeruginosa (58) and therefore is predicted to be responsible for the activation of acetate into acetyl-CoA during ethanolamine catabolism. The results of the current study suggest that the EBP PA4021 activates transcription of the PA4022-eat-eutBC operon from an RpoN promoter in response to acetaldehyde; a mechanism that is essential for ethanolamine catabolism.