FIG 5.
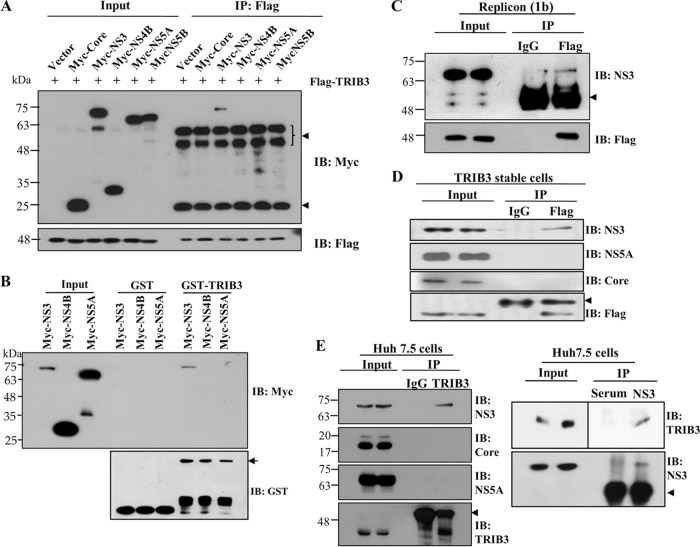
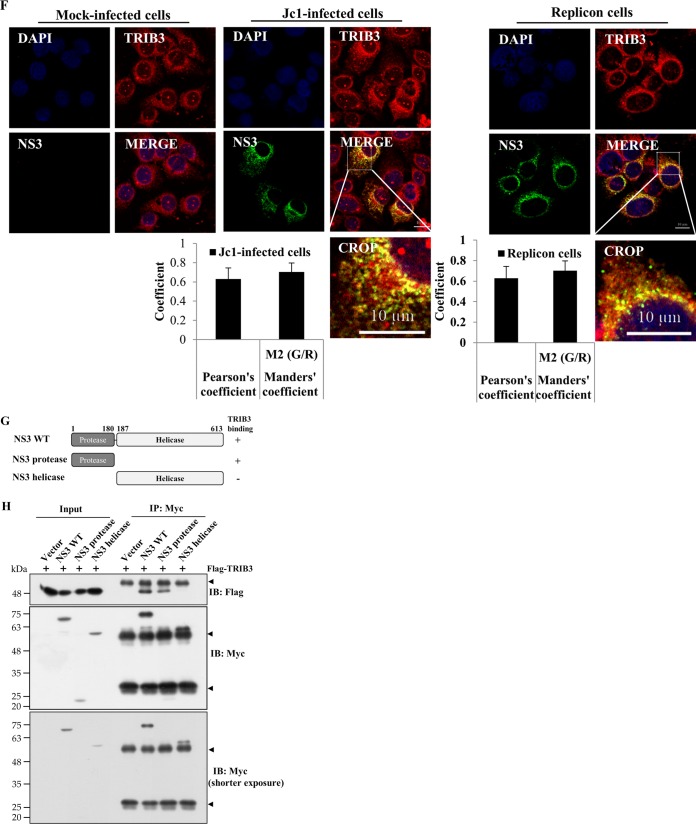
TRIB3 interacts with the protease domain of NS3. (A) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with Flag-tagged TRIB3 and the vector, Myc-tagged core, NS3, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B, individually. Twenty-four hours after cotransfection, total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-Flag antibody, and bound proteins were then analyzed by immunoblot (IB) analysis using an anti-Myc antibody. The arrowheads denote IgG. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged NS3, NS4B, and NS5A plasmids. Twenty-four hours after transfection, total cell lysates were harvested and incubated with either purified GST- or GST-TRIB3-conjugated glutathione beads. (Top) Bound proteins were detected by immunoblot analysis with an anti-Myc antibody. (Bottom) Protein expression levels of GST and GST-TRIB3 were verified by using an anti-GST antibody. The arrow indicates GST-TRIB3. (C) Huh7 cells harboring the HCV subgenomic replicon were transfected with a Flag-tagged TRIB3 expression plasmid. Thirty-six hours after transfection, total cellular extracts were immunoprecipitated with either mouse control IgG or mouse anti-Flag antibody. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-NS3 antibody. The arrowhead indicates IgG. (D) Huh7 cells stably expressing the TRIB3 protein were electroporated with in vitro-transcribed Jc1 RNA. Four days after electroporation, total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with either mouse control IgG or mouse anti-Flag antibody. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. The arrowhead denotes IgG. (E, left) Huh7.5 cells were electroporated with in vitro-transcribed HCV Jc1 RNA. Four days after electroporation, total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with either mouse IgG or an anti-TRIB3 antibody, and bound proteins were then immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Right) The same cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with either rabbit control serum or rabbit anti-HCV NS3 serum, and bound protein was then immunoblotted with an anti-TRIB3 antibody. The arrowheads denote IgG. (F, left) Huh7 cells seeded onto coverslips were either mock infected or infected with Jc1. At 4 days postinfection, cells were fixed in cold methanol at −20°C for 5 min, and immunofluorescence staining was performed by using an anti-TRIB3 monoclonal antibody and TRITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG to detect TRIB3 (red) and a rabbit anti-NS3 antibody and FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG to detect NS3 (green). (Right) Huh7 cells harboring the HCV subgenomic replicon were seeded onto coverslips and fixed in cold methanol at −20°C for 5 min. Immunofluorescence staining was performed as described above. Dual staining shows colocalization of TRIB3 and NS3 as yellow fluorescence in the merged images. Cells were counterstained with DAPI to label nuclei (blue). The enlarged selection marked by a white square is shown as a crop image. Colocalization of TRIB3 and HCV NS3 was verified by both Pearson's and Manders' overlap coefficients. More than 10 cells were applied to ImageJ analysis for quantification of the overlap coefficient, and error bars indicate the standard deviations of the means. G/R, ratio of green and red fluorophore colocalization. (G) Schematic illustration of the domain structure of the NS3 protein. (H, top) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with Flag-tagged TRIB3 and various constructs of Myc-tagged NS3. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Myc antibody, and bound proteins were immunoblotted by using an anti-Flag antibody. (Middle and bottom) Immunoprecipitation efficiency was verified by immunoblot analysis using the same cell lysates with an anti-Myc antibody. The arrowheads denote IgG.