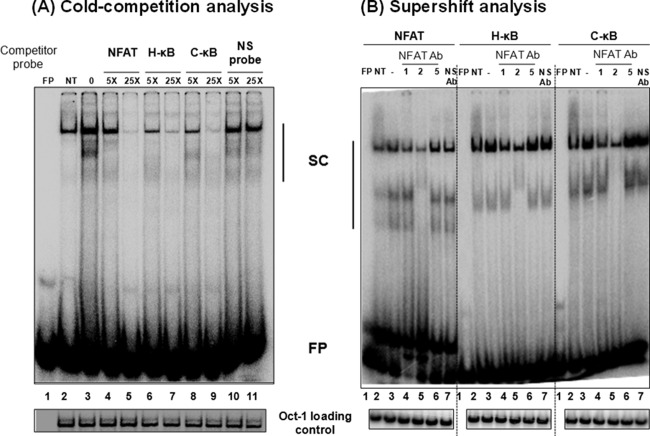
FIG 7.
C-κB probe binds NFAT regardless of genetic variation. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift analysis. A radiolabeled double-stranded DNA probe (40,000 cpm), derived from the IL-2 promoter sequence and containing an NFAT binding site, was incubated with 30 μg of the nuclear extract prepared from Jurkat cells after PMA/ionomycin activation for 1 h or control cells without activation. The cold competition was performed by incubating the complexes with a 5- or 25-fold excess of cold probes (NFAT, H-κB, C-κB, or a nonspecific probe). (B) Supershift analysis. Thirty micrograms of total protein of the nuclear extract prepared from PMA/ionomycin-induced Jurkat cells was preincubated with 2 μg of antibodies specific to NFAT1, NFAT2, or NFAT5 before the addition of radiolabeled NFAT, H-κB, or C-κB probes. Oct-1 was used as a loading control. FP, free probe; NS, nonspecific probe; NS Ab, nonspecific anti-p24 antibody; NT, no PMA/ionomycin treatment; SC, shifted complexes. The data are representative of three independent experiments.