TABLE 1.
Animal groups
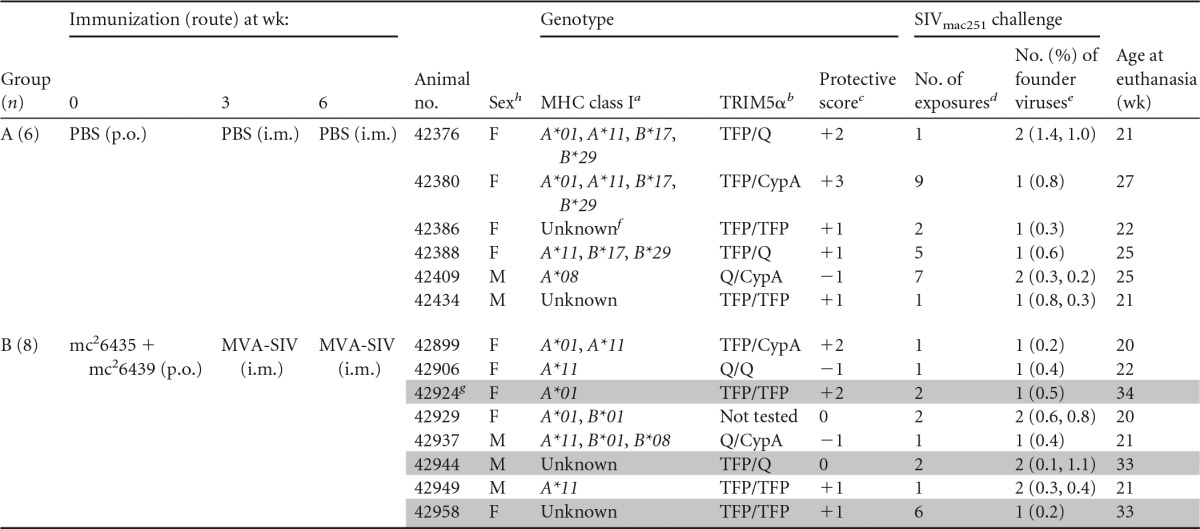
a The alleles Mamu-A*01, -B*08, and -B*17 have been associated with better disease outcome, whereas allele Mamu-B*01 is associated with higher viremia.
b The TRIM5α genotypes TFP/TFP and TFP/Cyp confer resistance to SIV infection, while the genotypes Q/Q and Q/CypA are associated with increased susceptibility to infection.
c Protective class I alleles and resistant TRIM5α alleles were assigned a value of 1. Genotypes associated with increased susceptibility or disease outcome received a score of −1. All other alleles were assigned a score of 0. The protective genotype score represents the sum of all scores for an individual animal (e.g., animal 42376 has MHC of 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 and TRIM5α of 0, for a score of +2).
d The number of exposures necessary to establish systemic infection.
e The number of founder viruses identified by SGA and gp160 sequencing of plasma virus isolated at weeks 1 to 2 postinfection. The numbers in parentheses indicate the percent difference from the inoculum consensus sequence for each viral clone analyzed.
f Unknown indicates not positive for any of the Mamu class I alleles tested (A*01, A*02, A*08, A*11, B*01, B*02, B808, B*04, B*17, and B*26).
g Vaccinated animals with better control of SIV replication are shaded in gray.
h F, female; m, male.
