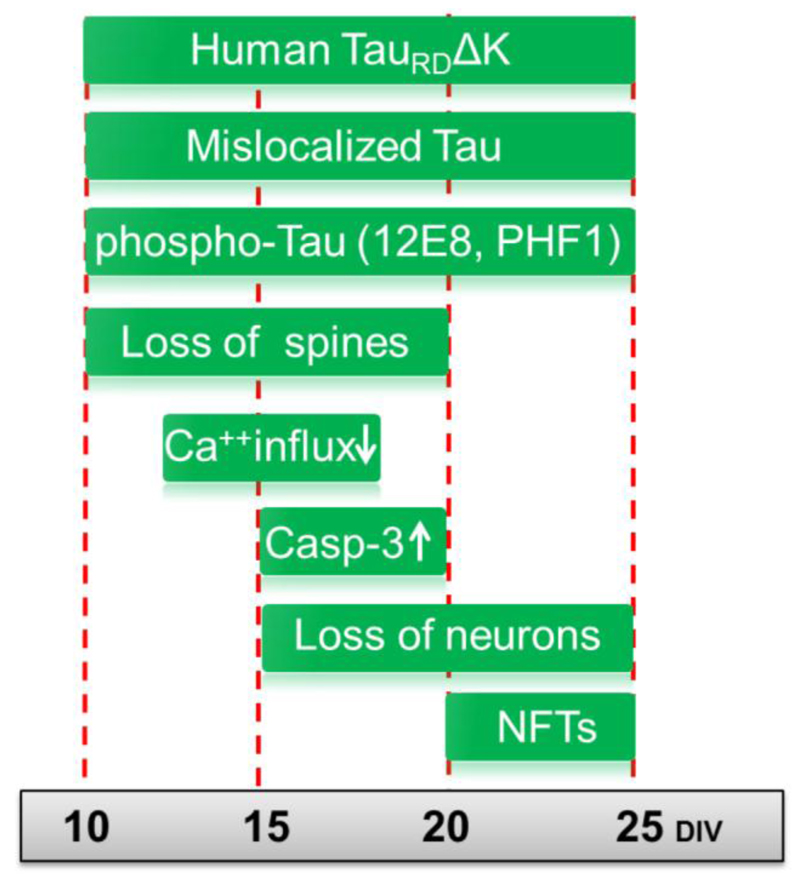
Fig. 7. Summary of pathological changes in pro-aggregant TauRDΔK slices.
TauRDΔK expressing mice were used for slice preparation at postnatal day 8. Cultures were analyzed up to 25 days in vitro (DIV). Early pathological events include the mislocalization of both endogenous and exogenous Tau into the somatodendritic compartment, observed already at DIV5 and remaining apparent until DIV25. From DIV10 onwards Tau becomes detectable in dendritic spines, and phospho-Tau appears in apical dendrites indicating mislocalization of endogenous Tau. At the same time (DIV10) the number of dendritic spines becomes strongly reduced. This is still observed at a later time point (DIV20), when spines in TauRDΔK slices are in an immature state. This effect is also observed in apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons and correlates with impairment in Ca++ dynamics, especially in stratum radiatum at DIV15. ThS positive Tau aggregates (neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs)), consisting of human and mouse Tau, are first detected at DIV20 and more prominently at DIV25. An increase in neuronal cell death (measured by LDH release, loss of NeuN) is first observed at DIV15 and increases further at DIV20 and DIV25. The activity of the apoptosis marker caspase 3 increases in parallel.