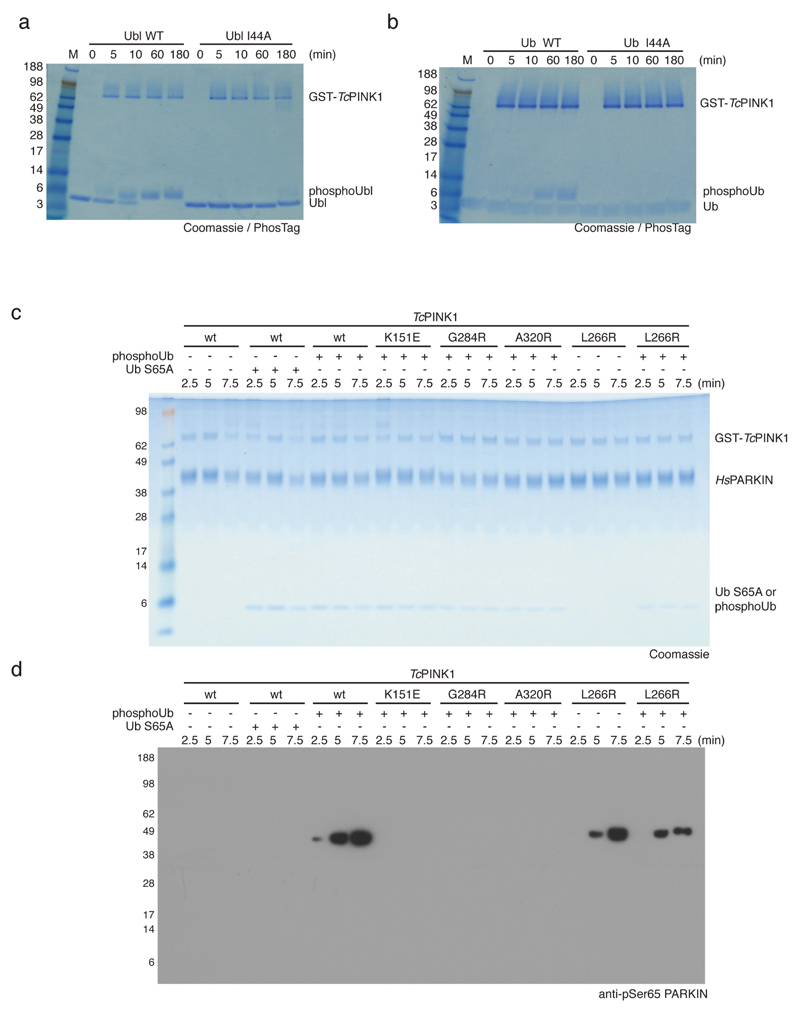
Extended Data Figure 7. The Ile44 patch is essential for PINK1-mediated phosphorylation of Ub and PARKIN Ubl, and controls for Fig. 4c.
All assays were performed three times with consistent results. (a-b) Coomassie stained PhosTag gels comparing the phosphorylation of (a) the HsPARKIN Ubl domain (aa 1-72) and (b) ubiquitin. In both cases, the wt form is compared with the I44A mutant form of the protein. GST-TcPINK1 does not efficiently phosphorylate the I44A mutants of ubiquitin or of the HsPARKIN Ubl domain. This is important since the Ile44 patch in the PARKIN Ubl domain is inaccessible and binds to RING1 in the structure of full-length RnPARKIN (4k95, 16) (see Fig. 4a). (c) Coomassie-stained gel for Fig. 4c with proteins labelled and (d) full-size blot for Fig. 4c.