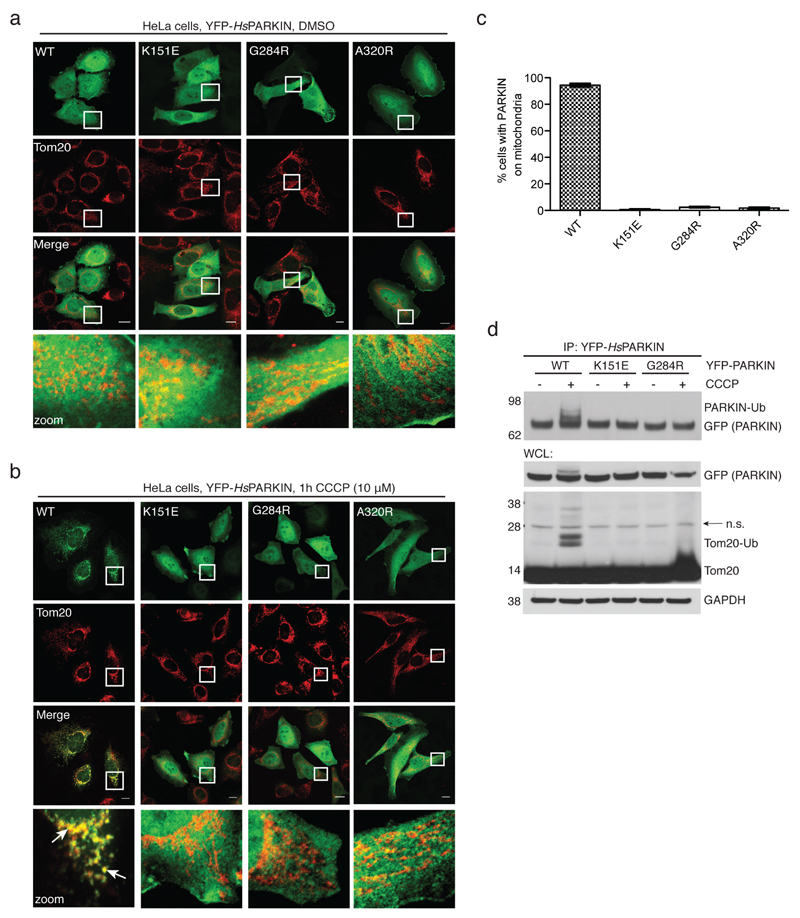
Extended Data Figure 4. PARKIN phosphoUb-binding mutants do not translocate to mitochondria.
(a-b) HeLa cells that do not contain detectable levels of PARKIN were transiently transfected with YFP-PARKIN wt and indicated mutants (green). Tom20 staining with anti-Tom20 antibody indicated mitochondria (red). Images are representative of three biological replicates. (a) In DMSO-treated control cells, PARKIN does not co-localize with mitochondrial Tom20. (b) After treatment with CCCP (10 µM) for 1h, wt PARKIN but not phosphoUb binding mutants co-localize with Tom20. Scale bars, 10 µm. Split channels are shown with overlay to illustrate co-localization. The YFP channel is identical to Fig. 2g. (c) Quantification of cells with PARKIN localized at mitochondria in b, scored for 150 cells per condition in three biological replicates. PhosphoUb binding mutants do not show sustained mitochondrial localization. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (d) HeLa cells transiently transfected with HsPARKIN wt and mutants were treated with CCCP and YFP-PARKIN immunoprecipitated (see Methods). Whole cell lysates (WCL) or immunoprecipitates (IP) were western blotted for PARKIN, Tom20 and GAPDH (loading control) as indicated. Ubiquitinated forms of PARKIN and Tom20 can be observed with wt PARKIN but not with PARKIN mutants. Also see Fig. 2h where in addition the A320R mutant was included. These experiments were performed three times as biological replicates with similar results. Note that PARKIN autoubiquitination varied and was weaker in some experiments, while Tom20 ubiquitination was more robust. See Supplementary Information for uncropped blots.