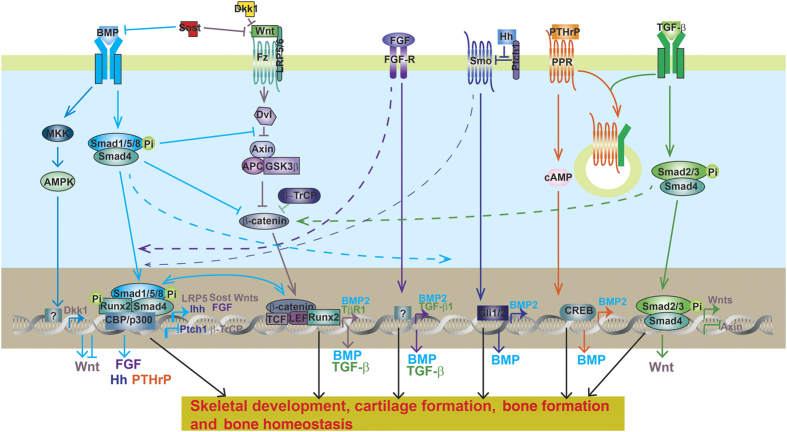
Figure 3.
Crosstalk between BMP, TGF-β, and other signaling during osteoblast differentiation. BMP has dual roles in Wnt signaling. On one hand, BMP inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling by increasing Wnt antagonist Dkk1 and Sost expression and by preventing β-catenin nuclei translocation. On the other hand, BMP promotes Wnt/β-catenin signaling by forming co-transcriptional complex with β-catenin/TCF/LEF/Runx2, by increasing Wnt expression, by antagonizing Dvl function and by decreasing b-TrCP expression. BMP signaling promotes FGF, Hh, PTHrP signaling by increasing IHH expression, increasing FGF expression, decreasing Ptch1 expression, respectively. BMP is essential for IHH-induced osteoblast differentiation. FGF, IHH, Wnt, and PTHrP signaling all promotes BMP2 expression so as to enhance BMP signaling. FGF and IHH signaling is essential for BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation. TGF-β antagonizes PTHrP signaling through TGF-β type II receptor complexing and internalizing together with PTHrP receptor (PPR). TGF-β promotes Wnt activity by increasing Wnt ligands expression and decreasing Axin expression. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and Wnt all increase TGF-β expression to promote TGF-β signaling. BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; PTHrP, parathyroid hormone-related peptide; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.