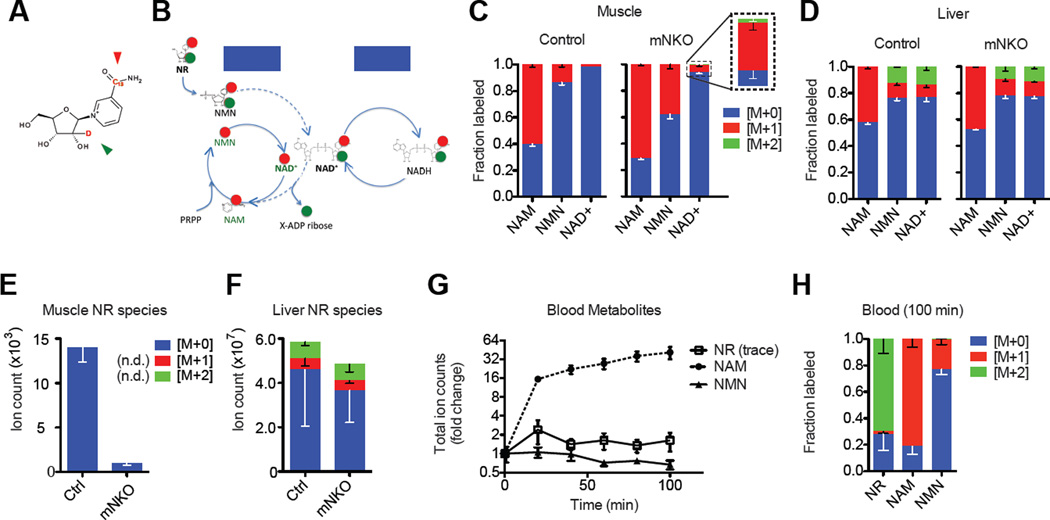
Figure 6. Oral bioavailability of NR to muscle.
A, Molecular structure of the NRM+2 mass isotopologue. Green and red arrows indicate locations of 13C and deuterium labels, respectively.
B, Schematic of proposed NRM+2 entry into the NAD salvage pathway (dashed lines, ATP omitted) and the subsequent separation of the isotopes on ribose and NAM moieties. Basal metabolic redox processes do not affect the arrangement of the labels.
C, Incorporation pattern of heavy isotopes into intermediates of the NAD salvage pathway in skeletal muscle and
D, Liver tissue 100 minutes after oral gavage with 200 mg/kg NRM+2 (n=3).
E, Detection of NR isotopologues in quadriceps muscle and
F, Liver tissue 100 minutes after oral gavage with 200 mg/kg NRM+2. Some isotopologues were not detected (n.d.) in muscle (n=3).
G, Appearance of blood metabolites after oral gavage with 200 mg/kg NRM+2 and
H, Fractional labeling in blood after 100 minutes (n=3 per genotype, pooled). NR was detected in trace amounts. Error bars represented SEM. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (ns, not significant, *p<0.05,**p<0.01). Mice were female aged 7 months.