FIGURE 1.
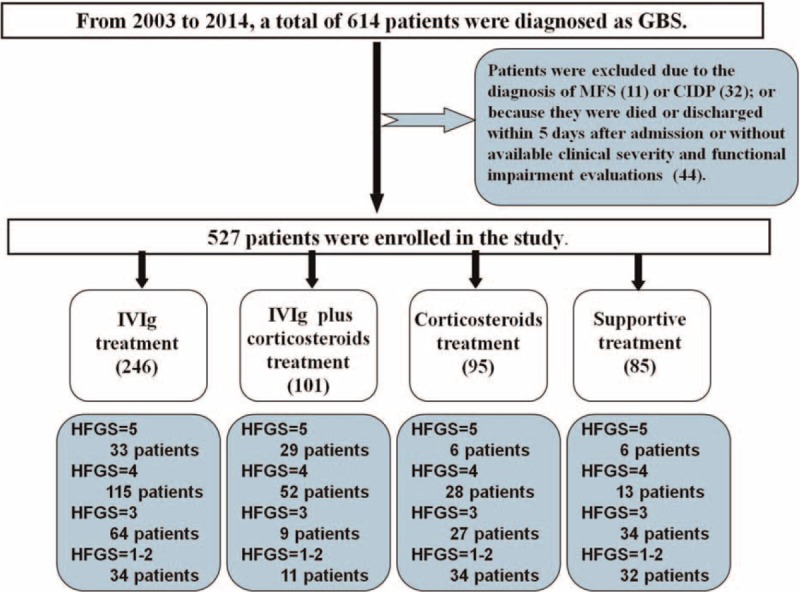
Flow chart of the study. From 2003 to 2014, a total of 614 patients who were admitted to the Department of Neurology of the First Hospital of Jilin University were diagnosed as Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS). Thirty-two patients with later-confirmed chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) and 11 patients with Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS) were excluded from the study. In addition, 44 patients who were died or discharged within 5 days after admission and those without available evaluations of the clinical severity and functional impairment during hospitalization were ruled out as well. Finally, 527 patients with GBS were enrolled and were divided into 4 groups according to the treatment modality, that is, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatment group (246 patients), IVIg plus intravenous corticosteroids treatment group (101 patients), intravenous corticosteroids treatment group (95 patients), and supportive treatment group (85 patients). In each group, according to the Hughes Functional Grading Scale (HFGS) score, the patients were further divided into different subgroups.
