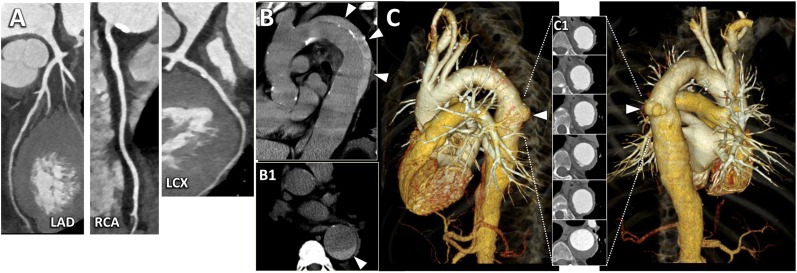
Figure 6.
A 60-year-old male with acute onset of chest pain radiating to the back and dyspnoea. Non-specific repolarization alterations were documented at electrocardiography (ECG). Initial troponin level was normal. A triple-rule-out examination using a thoracoabdominal prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition with a dedicated contrast media injection protocol was performed. (a) CT angiography acquisition demonstrated a normal left anterior descending artery (LAD) and only mild atherosclerosis (stenosis <30%) at the proximal segment of the left circumflex artery (LCX) and right coronary artery (RCA). (b) In the left parasagittal plane, pre-contrast acquisition revealed a Type-B intramural haematoma (arrowheads) involving the descending thoracic aorta. The corresponding cross-section view delineated the semi-circumferential extension of the intramural haematoma (arrowhead in Panel b1). (c) Three-dimensional volume-rendering reconstructions of the thoracic vascular structures in the left lateral (left) and posterior (right) views, revealed an ectatic descending thoracic aorta with an ulcer-like projection at the middle level (arrowheads). Note the corresponding cross-section images showing the ulcer-like projection and the intramural haematoma (Panel c1) and the normally perfused pulmonary system.