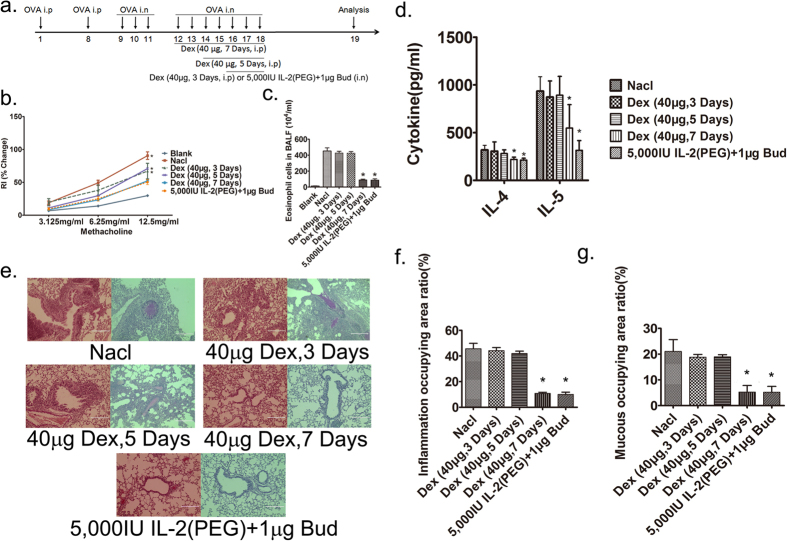
Figure 4. Manifestations of allergic airway disease after administration of different drugs.
IL-2(PEG) combined with budesonide can achieve the same curative effect as regular therapy of systemic use of dexamethasone. (a) Timeline of drug intervention and analysis. Female BALB/c mice were immunized with OVA i.p on days 1 and 8, followed by intranasal (i.n) 2% OVA challenges on days 9–14. For i.n group, 5,000 IU IL-2(PEG) plus 1 μg budesonide were administrated intratracheally on days 16–18. For i.p groups, 40 μg dexamethasone was injected intraperitoneally on days 12–18, 14–18 or 16–18. On day 19, mice were sacrificed and analyzed. (b–g) To prove the efficacy of the combination of IL-2(PEG) plus budesonide compared with traditional treatment, we measured AHR, eosinophil counts and Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-5 in BALF and images of lung sections (scale bars, 200 μm) in asthma model mice treated with 40 μg dexamethasone (Dex) intraperitoneally for 3, 5 or 7 days or treated with 5,000 IU IL-2(PEG) plus 1 μg budesonide (Bud) for 3 days. Results represent the changes in lung resistance (Rl) as a measure of AHR. *p < 0.05. (b–d,f,g) Data are presented as means ± SEM (n ≥ 4 per group and data point); here representative results from 1 of 2 experiments are shown. Treated group versus blank group (c) or Nacl group (d) by Student’s t test. (d) Left, H&E staining; right, PAS staining. i.n., intranasal; i.p., intraperitoneal. Blank group, health control mice. Nacl group, asthma model mice treated with normal saline.