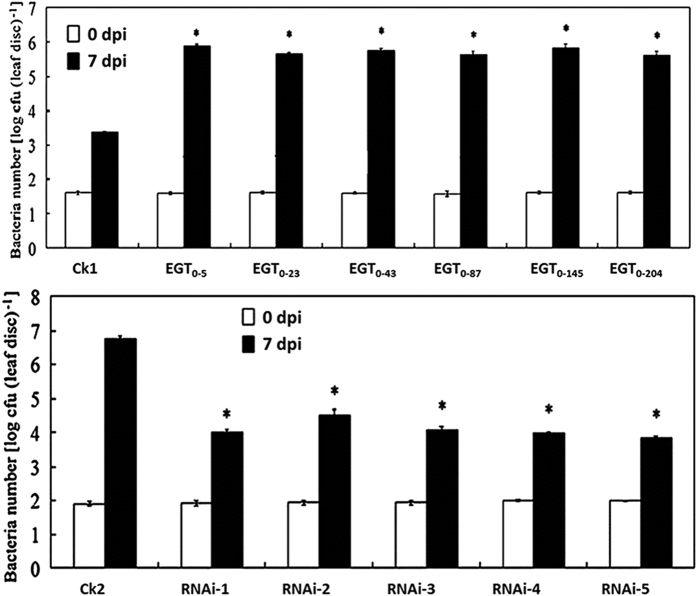
Figure 8. Measurement of bacterial growth in transgenic eggplants.
Briefly, using the syringe inoculation method, bacteria wilt was scraped off a fresh plate, resuspended in sterile water to 105 colony-forming units (c.f.u.) ml−1, and pressure-infiltrated into leaves with a needleless syringe. After 7 days, leaves were harvested and surface sterilized (30 s in 70% ethanol, followed by 30 s in sterile distilled water) for the spray inoculation method. Leaf discs from different leaves were ground in 10 mM MgCl2 using a microfuge tube glass pestle. After homogenization, the samples were thoroughly vortex-mixed and diluted 1:10 serially. Samples were finally plated on TZC solid medium (3 g casein hydrolysate, 5 g peptone, and 10 g glucose (pH 7.0). The plates were incubated at 28 °C for 2 days, after which the colony-forming units were counted. CK1 represents non-transgenic plants from the E-31 line; EGT0–87, EGT0–145, and EGT0–204 are the SmNAC overexpressing transgenic eggplants (T0). CK2 represents non-transgenic plants from the E-32 line; RNAi-1, -2, -3, -4, and -5 are RNAi-SmNAC transgenic plants (T0). Error bars represent standard error, and the experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results. Asterisks indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05 compared with the non-transgenic plants.