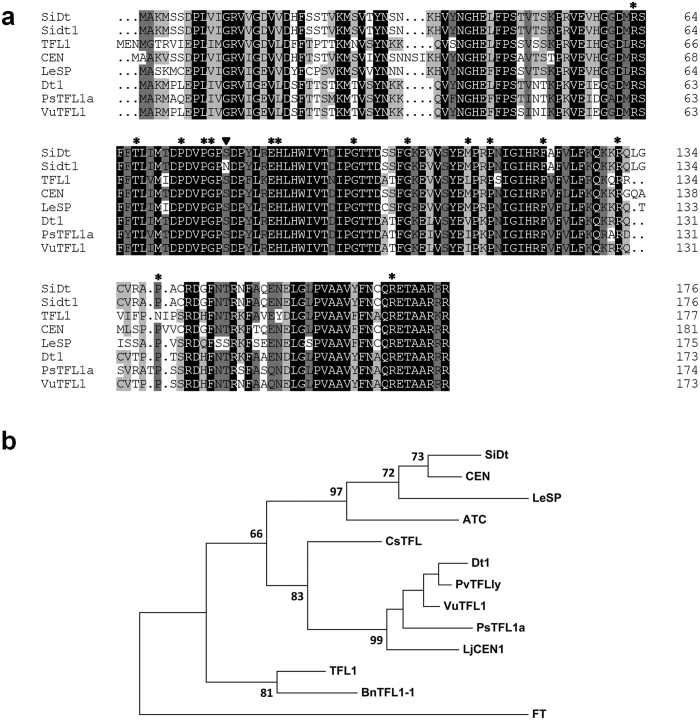
Figure 4. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences of SiDt and Sidt1 with their homologues in other plant species.
(a) Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequences of SiDt and Sidt1 (S. indicum) with those of TFL1 (A. thaliana), CEN (A. majus), LeSP (L. Esculentum), Dt1 (G. max), PsTFL1a (P. sativum) and VuTFL1 (V. unguiculata). Asterisks above the amino acid sequences indicate amino acid residues which vary among TFL1 homologues (but not in the homologues aligned here). The arrowhead indicates the S79N mutation site in the Sidt1 protein. Identical residues are shaded in black; conserved residues are shaded in gray; residues with low identity are shaded in light gray. The black dot indicates an amino acid gap. (b) Phylogenetic tree of different TFL-homologs generated using the maximum likelihood method. Numbers above the branches indicate the support with 1000 bootstrap replications. The cluster includes SiDt protein and homologs TFL1 (AAB41624, A. thaliana), ATC (BAA75932.1, A. thaliana), CEN (AAB36112, A. majus), LeSP (AAC26161, L. esculentum), Dt1 (ADF30893, Glycine max), PvTFLly (AFI47668, P. vulgaris), PsTFL1a (AAR03725, P. sativum), VuTFL1 (AIA10354, V. unguiculata), CsTFL (NP_001275848, C. sinensis), LjCEN1 (AAQ93599, L. japonicas), BnTFL1-1 (BAA33415, B. napus) and FT (BAA77838, A. thaliana).