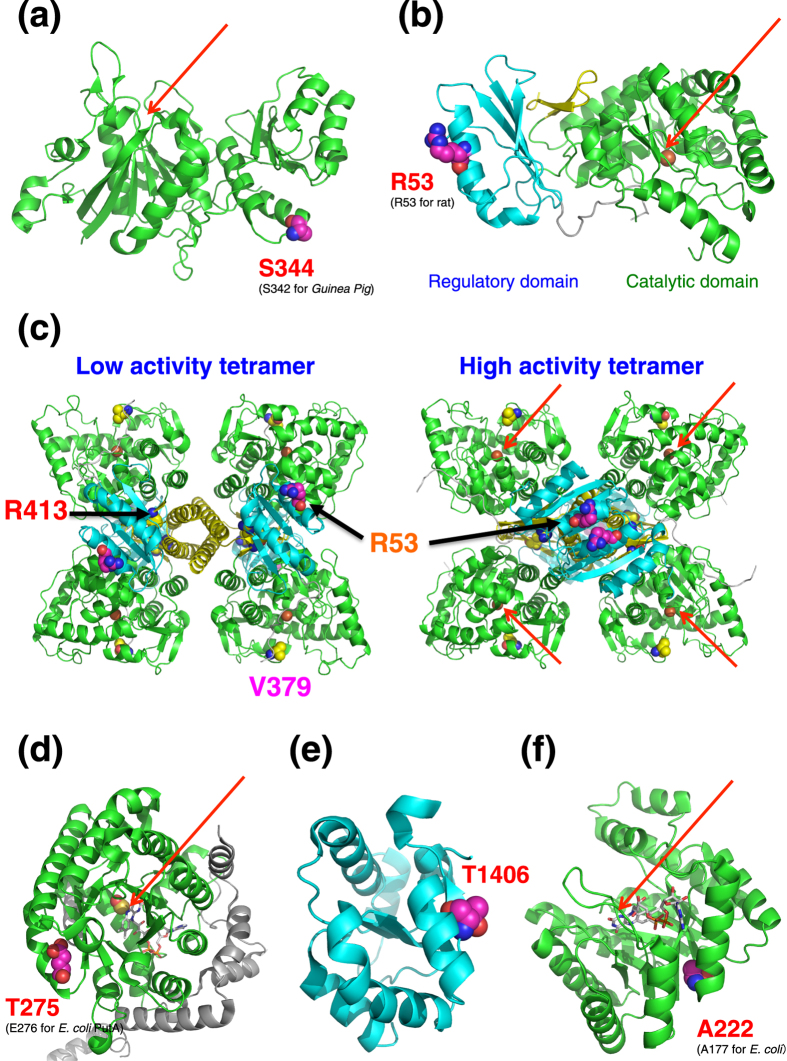
Figure 5. Mapping of the five non-synonymous variants on the reported crystal structures of the enzymes, respectively.
Ribbon models of (a) structure of Guinea pig L-Asparaginase 1 Catalytic domain (Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID: 4R8 K), (b) structure of rat phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) (PDB ID: 2PHM), (c) two types of tetramer model structures of PAH, low activity tetramer and high activity tetramer, (d) structure of E. coli PutA proline dehydrogenase domain (PDB ID: 2FZM), (e) structure of human carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1) regulatory domain (PDB ID: 2YVQ), and (f) structure of E. coli methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) (PDB ID: 1B5T) are shown. The catalytic domains are depicted in green, whereas the regulatory domains are depicted in cyan. In the case of PAH structure, the C-terminal tetramerization domain is depicted in yellow. The residue corresponding to the position of each non-synonymous variant is shown by a sphere model. Cofactor FADs were represented by stick model for PRODH and MTHFR. The catalytic site of each enzyme is indicated by red arrow. The coordinates of the human PAH tetramers were obtained from the supplementary data of the reported article15. All figures were made using the PyMOL Software Package (https://www.pymol.org/).