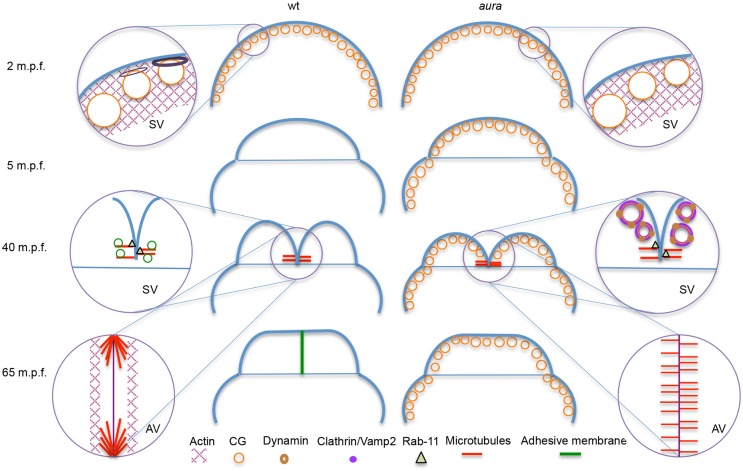
Fig. 11.
Summary of the effects on cytoskeletal and membrane dynamics observed in aura/mid1ip1l early mutant embryos. Key processes in early wild-type embryos (left) and defects in aura/mid1ip1l mutants (right), focusing on cytoskeletal dynamics and exocytosis of internal membrane. In mutants, during egg activation CGs fail to be released, possibly owing to the inability to restructure cortical actin. During furrow formation, the microtubule-based FMA fails to reorganize and pericleavage F-actin-rich regions are reduced. Failure of pericleavage F-actin enrichment and sequestration of CG internal membrane in mutants results in the inability to form interblastomere adhesive membrane. Exocytic and endocytic components, such as Vamp2, Clathrin and Dynamin 2, become localized to unreleased CGs in mutants and are unavailable. The exocytic factor Rab11 exhibits normal furrow localization in the mutants. AV, animal view; SV, side view.