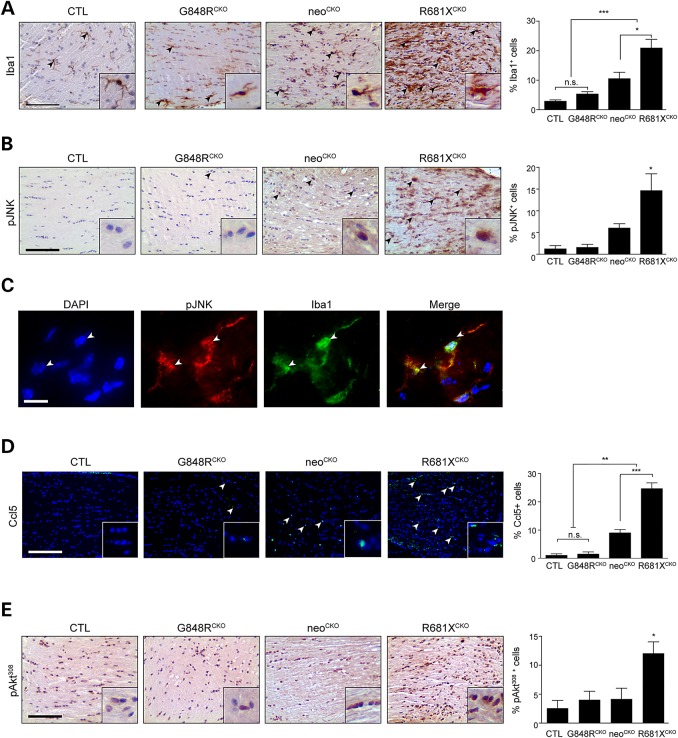
Figure 5.
Optic glioma formation and growth is partly determined by the effect of the germline Nf1 gene mutation on microglia number and function. (A) Iba1 immunostaining demonstrates increased numbers of microglia in the optic nerves of neoCKO (3.6-fold) and R681XCKO (7.1-fold) mice relative to controls (CTL). Whereas R681XCKO mice have more microglia than neoCKO mice (2-fold), no increase in microglia numbers was detected in G848RCKO mice relative to controls (n = 5 mice per genotype). (B) Increased percentages of pJNK+ cells were observed in neoCKO (4.66-fold) and R681XCKO (11.28-fold) optic nerves relative to control optic nerves (n = 4 mice per genotype). (C) Immunofluorescence revealing pJNK staining in Iba1+ cells (microglia) within the optic nerves of R681XCKO mice. White arrowheads depict two independent cells positively labeled with both pJNK and Iba1. (D) Increased percentages of CCL5+ cells were observed in neoCKO (14.56-fold) and R681XCKO (27.37-fold) optic nerves compared with control mice (n = 5 mice per genotype). (E) A greater percentage of pAktThr308-immunoreactive cells was found in R681XCKO mice relative to control (4.68-fold), and neoCKO (2.88-fold) optic nerves (n = 4 mice per genotype). Scale bars: 100 µm. All data are represented as means ± s.e.m. (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test).