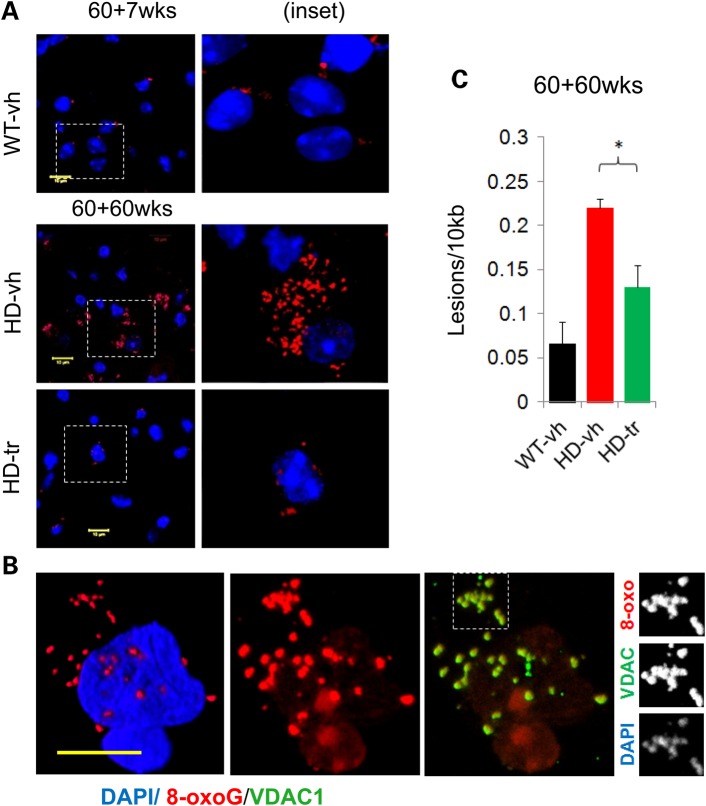
Figure 6.
XJB-5-131 reduces oxidative damage in MT and somatic DNA. (A) At the start of treatment there are = low levels of oxidative DNA lesions in untreated HdhQ(wt/wt) (WT-vh) animals as visualized by anti-8-oxo-G IF staining. There is little discernible difference between WT and HdhQ(150/150) (HD) littermates at these early ages (up to 85 weeks of age) (image not shown). At late ages (120 weeks), there is a multi-fold increase in DNA lesions in HD animals, which is suppressed by XJB-5-131 treatment, as seen both by IF staining for 8-oxo-G (A,B) and by (C) q-PCR analysis (n = 3 mice per group) (*P < 0.05) (P = Student's t-test, one-tailed homoscedastic). (B) 8-oxo-dG (red) is present both in MT and in the nucleus of striatal cells of old HD mice [in this case an HdhQ(150/150)-vh mouse 120 weeks of age]. (B, Panel 2) The localization of the oxidative damage is primarily perinuclear foci, along with a fainter and diffuse nuclear pattern. (B, Panel 3 and insets) The foci co-localize with the MT [anti-VDAC (green)] and also with DAPI (viewable when DAPI imaging exposure is increased). Yellow bars represent 10 µm (images ∼21 µm confocal Z-stack 3D reconstruction, frame: 84.9 µm2).