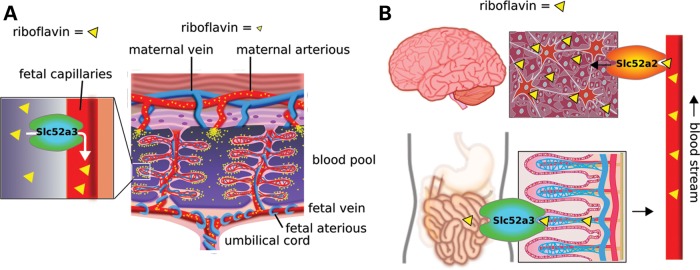
Figure 7.
Scheme of the SLC52A3 function in embryo development and BVVL patients. (A) Mechanism of riboflavin absorption in mouse placenta. Embryo vein absorbs riboflavin from the intervillus blood pool in which maternal blood supplies essential nutrients. Riboflavin is suggested to be absorbed through Slc52a3 to the fetal vein and supplied to fetus through umbilical cord. (B) A hypothesis of pathogenesis in BVVL syndrome. SLC52A3 in the intestine and spinal cord. Riboflavin is absorbed in the intestine through SLC52A3 transport. Riboflavin is expected to be absorbed from the blood stream to neural tissues via SLC52A2.