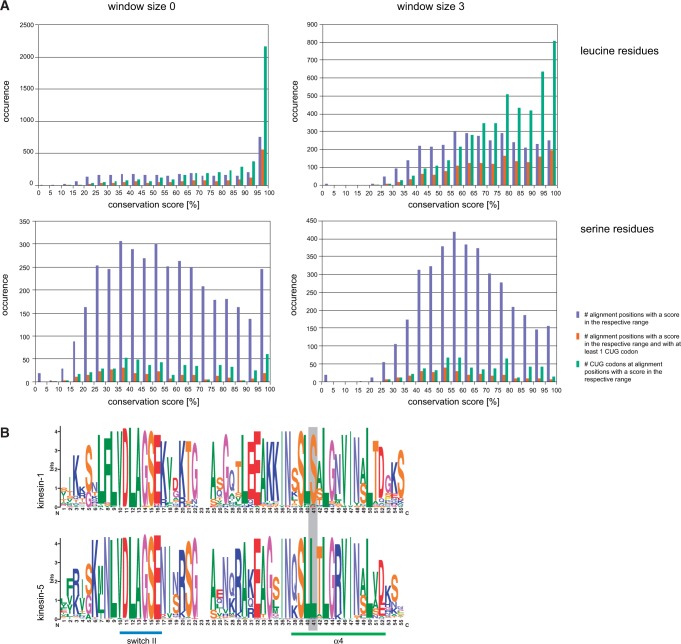
Fig. 3.—
Conservation of serine and leucine positions. (A) The charts show the amino acid conservation at all alignment positions of the Gblocks reduced concatenated alignment of the 26 cytoskeletal and motor proteins, at which at least one leucine (upper charts) or one serine (lower charts) is present. The sequence conservation has been determined based on the property-entropy divergence, as described in Capra and Singh (2007). With a window size of 0, each column is scored independently (left row), whereas the surrounding three columns are also taken into account with a window size of 3 (right row). Blue bars represent the number of alignment positions with a conservation score for leucine and serine residues, respectively, within the given half-bounded intervals. Red bars denote the number of alignment positions with respect to conservation, at which at least one CUG codon is present independent of its translation. Green bars give the total numbers of CUG codons at the respective alignment positions. (B) The weblogos (Crooks et al. 2004) show the sequence conservation of two kinesin subfamilies, kinesin-1 and kinesin-5, within the family-defining motor domain around the highly conserved switch II and α-helix α4 motifs. At the position within α4 marked by a grey bar, kinesin-1 sequences contain a highly conserved serine whereas kinesin-5 sequences contain a highly conserved leucine indicating the need to resolve subfamily relationships when determining CUG codon usage by sequence conservation.