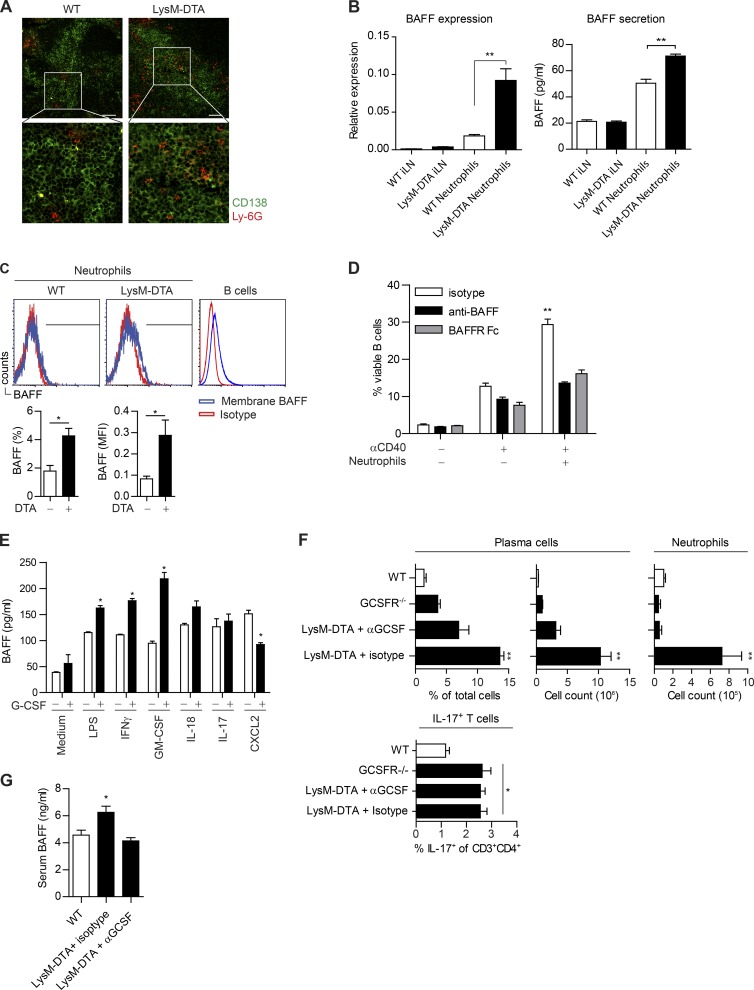
Figure 8.
Neutrophils are localized close to plasma cells and produce BAFF in a G-CSF–dependent manner. (A) Immunofluorescent staining of iLNs at day 14 after CFA to visualize plasma cells (CD138+; green) and neutrophils (Ly-6G+; red). Bars, 50 µm. (B) Sorted neutrophils (purity >90%) from day 14 iLNs. WT iLNs and LysM-DTA iLNs are the neutrophil-depleted cell fraction. BAFF expression was normalized to HPRT. Measurement of BAFF in supernatants from sorted LysM-DTA and WT iLN neutrophils 14 d p.i. Neutrophils were cultured at a density of 105 cells/well for 24 h. (C) Neutrophils (CD11b+Ly-6G+) were analyzed for membrane-bound BAFF in the iLN at day 14. Isotype mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was subtracted from BAFF mean fluorescence intensity. B220+ B cells were used as a positive control. (D) B cells were sorted from WT spleen, and neutrophils were sorted from WT BM. 106 B cells were co-cultured at a 1:1 ratio with neutrophils and 30 µg/ml anti-CD40 for 72 h. 5 µg anti-BAFF or 5 µg BAFF receptor (BAFFR) Fc was used to neutralize BAFF. (E) Sorted BM neutrophils (>95% purity) were cultured in a 48-well plate at a density of 5 × 105 cells in 500 µl of medium and stimulated for 6 h with the respective stimuli. (F) Analysis of the presence of plasma cells and neutrophils in iLNs at day 14 p.i. in WT, GCSFR−/−, and LysM-DTA mice treated with an anti–G-CSF neutralizing antibody (67604) or isotype control. Mice were given i.p. injections of 5 µg of antibody on day 0 and every second day until day 14. (G) BAFF-ELISA of serum samples collected at 14 d after CFA in WT and LysM-DTA mice treated with neutralizing anti–G-CSF or rat isotype antibody. Data in A are representative of four separate mice. Data in B–G are representative of two separate experiments. n = 5/group. Results are mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (unpaired Student’s t test).