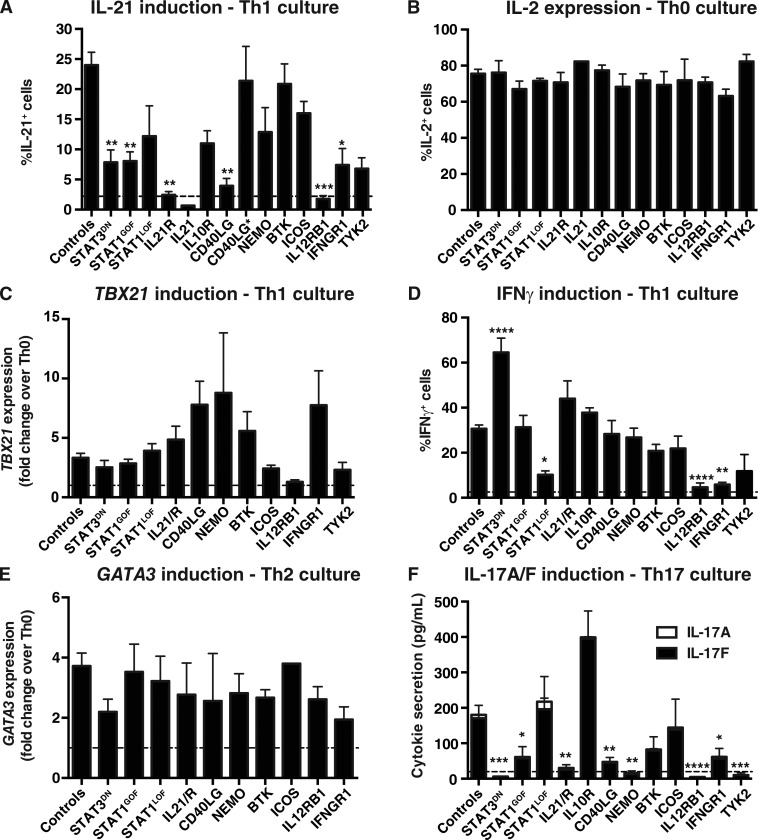
Figure 4.
Impact of disease-causing mutations on differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells to Th1, Th2, Th17, and Tfh fates in vitro. Naive CD4+ T cells were isolated from peripheral blood of healthy donors or patients with mutations in STAT3, STAT1, IL21/R, IL10R, CD40LG, NEMO, BTK, ICOS, IL12RB1, IFNGR1, or TYK2, and then cultured with TAE beads alone (Th0) or under Th1/Tfh (+IL-12), Th2 (+IL-4), or Th17 (+TGF-β, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-21, and IL-23) conditions for 5 d. Cells were then harvested and analyzed for expression of cytokines and transcription factors. (A) Percentage of cells expressing IL-21 in response to Tfh/IL-12 stimulation. (B) Percentage of cells expressing IL-2 in Th0 culture. (C and D) Induction of TBX21 (C) and IFN-γ (D) expression after Th1/IL-12–polarizing culture. (E) Induction of GATA3 in response to Th2/IL-4 stimulation. (F) Induction of IL-17A and IL-17F secretion after Th17-polarizing culture. Controls, n = 17–48; STAT3DN, n = 2–10; STAT1GOF, n = 5–14; STAT1LOF, n = 3–8; IL21R, n = 3–5 experiments; IL21 n = 1; IL10R, n = 1–2; CD40LG, n = 3–9 (CD40LG* (MILD), n = 3); NEMO, n = 2–7; BTK, n = 5–8; ICOS, n = 2–7; IL12RB1, n = 3–8; IFNGR1, n = 2–6; TYK2, n = 2–3. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001, compared with Th0 (ANOVA; Student’s t test). The dashed lines indicate the mean percentage of IL-21+ (A) or IFN-γ+ (D) cells, or secretion of IL-17A/F (F), detected under Th0 conditions. Note that data for IL-17A/F production by TYK2-deficient naive CD4+ T cells was presented in Kreins et al. (2015), but is shown here for comparison.