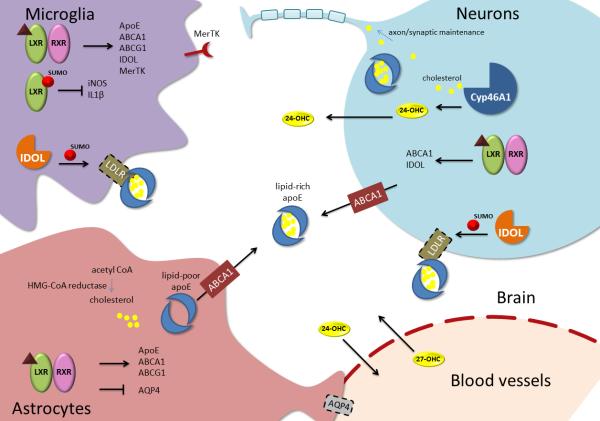
Figure 2, Key Figure. Cell type-specific roles of cholesterol metabolism and LXR signaling in the CNS.
Bottom left, astrocytes are the major producers of cholesterol in the CNS, and HMG-CoA reductase mediates conversion of acetyl CoA to cholesterol. ApoE, the major protein constituent of the HDL-like complexes that transport cholesterol from astrocytes throughout the CNS, is transcriptionally regulated by LXR along with its lipidating transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1. Nascent apoE is packaged with cholesterol and other lipid species by ABCA1 and released from the cell as HDL-like particles. Additionally, LXRs inhibit astrocytic expression of AQP4 and therefore participate in regulation of water transport at the BBB. Bottom right, oxysterols but not cholesterol may cross the BBB. The exchange of CNS-synthesized 24-OHC and peripherally synthesized 27-OHC allows communication between brain and periphery regarding cholesterol metabolism. Upper right, neurons use cholesterol for maintenance of axons and synapses, which is required for their proper function. Adult neurons rely on cholesterol delivery by astrocyte-synthesized apoE, which is recognized and endocytosed by members of the LDLR family. In conditions of excess cholesterol, neuronal Cyp46A1 converts cholesterol to 24-OHC, which can diffuse through the membrane and also acts as a ligand for LXR. In neurons, LXR activation lowers intracellular cholesterol by promoting transcription of ABCA1, which loads cholesterol onto apoE. Additionally, the E3 ubiquitin ligase IDOL mediates the SUMOylation of LDLR family members, leading to their endocytosis and degradation and therefore decreased cellular uptake of lipids. Upper left, microglia, like astrocytes, produce and lipidate apoE in an LXR-dependent manner. As in neurons, LXRs in microglia transcriptionally regulate IDOL and therefore surface expression of LDLRs. Additionally, in microglia LXRs regulate expression of phagocytic genes such as MerTK, and SUMOylated LXRs mediate transrepression at pro-inflammatory promoters.