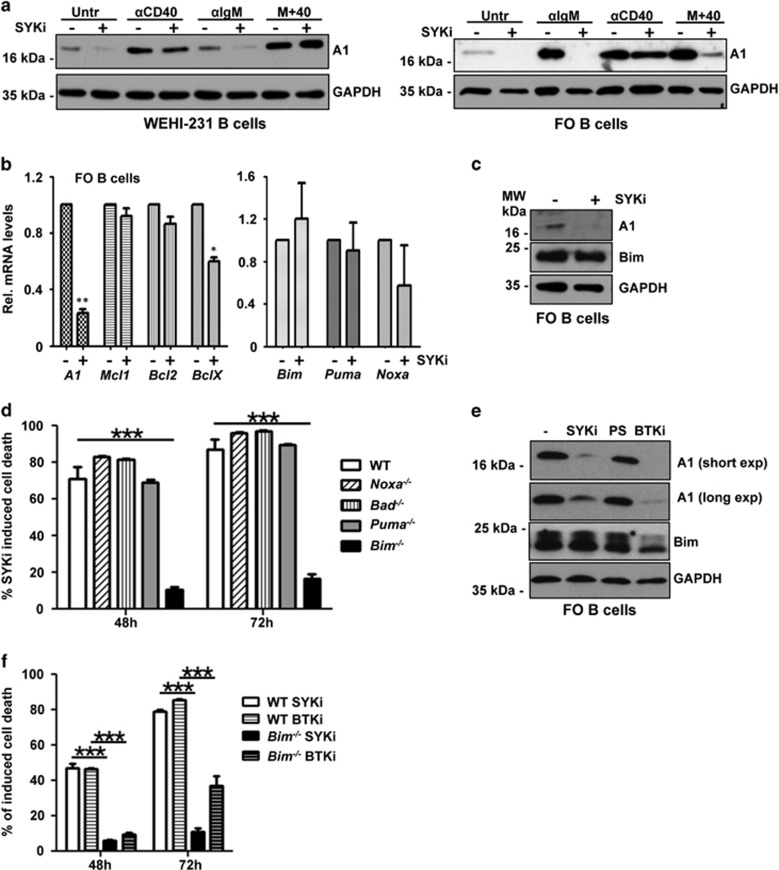
Figure 7.
Inhibition of Syk or Btk reduces A1 expression and triggers Bim-dependent apoptosis. (a) WEHI-231 B cells or sorted FO B cells from wild-type mice were left untreated or treated with 2 μM of the Syk inhibitor R406 and stimulated as indicated for 4 h. Cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody specific for mouse A1 or GAPDH to control for protein loading (one out of two independent experiments yielding similar results is shown). (b) Sorted follicular B cells were stimulated for 6 h with Syk inhibitor or solvent control. RNA was isolated for qPCR analysis. Bars represent means±S.E.M. (n=3). (c) A1 and Bim protein levels were assessed 4 h after inhibitor treatment (5 μM) by western analysis. (d) FO B cells from mice of the indicated genotypes were sorted and cultured in the absence or presence of 5 μM Syk inhibitor. Survival was monitored by Annexin V staining. Bars represent means±S.E.M. (n=3). (e) Comparison of A1 and Bim protein levels 4 h after 5 μM Syk inhibitor, 10 μM PS-1145 (Ikk) inhibitor or 5 μM Btk inhibitor treatment of sorted splenic B cells pretreated for 24 h with anti-IgM by western analysis. (f) Comparison of FO B-cell survival after inhibition of Syk or Btk (5 μM). *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001