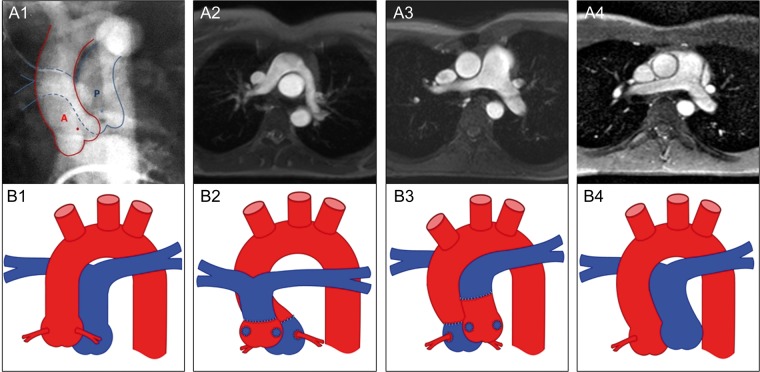
Figure 1:
Morphology of the pulmonary arteries. Preoperative cinecardioangiogram (anterior–posterior projection) of a patient with simple D-TGA showing the centre points of the aortic (red dot) and pulmonary root (blue dot) (1). Anatomy of the great arteries 20 years after primary ASO, comparing the Lecompte technique (2) and the spiral anastomosis (3) and normal configured pulmonary arteries in a healthy control (4) illustrated by MRI (axial views) (upper row) and as a schematic drawing (lower row, red colour: aorta, blue colour: pulmonary artery). The steep aortic arch is illustrated by the smaller distance between the ascending and descending aorta in the Lecompte technique and the riding of the pulmonary bifurcation on the aorta. The post rotational more leftward position of the pulmonary root is shown in a patient with a spiral anastomosis (3a) and the corresponding schematic drawing (3b). A: aorta; P: pulmonary artery; D-TGA: dextro-transposition of the great arteries; ASO: arterial switch operation; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.