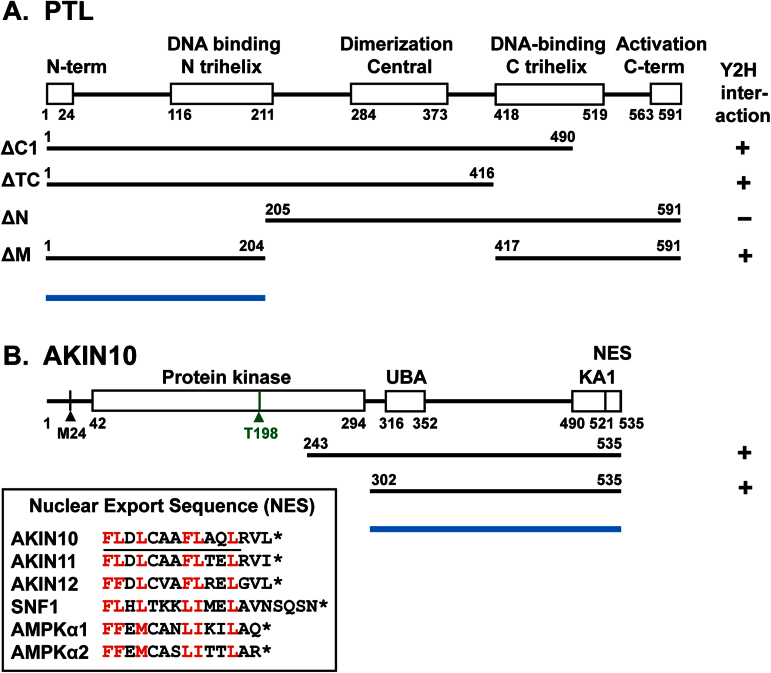
Fig. 1.
Maps of PTL and AKIN10, showing the results of yeast two-hybrid interactions. (A) Map of the PTL protein, showing the conserved trihelix DNA-binding domains, the central dimerization domain, and two terminal domains. BD–PTLΔC1, used in the library screen, removes a C-terminal activation region. The extent of other deletions used in yeast two-hybrid tests, and the results of these tests with AD–AKIN10, are shown. (B) Map of the AKIN10 protein, with functional domains predicted by Pfam. These are a kinase domain that includes a phosphorylated threonine at codon 198 (green), a ubiquitin-associated domain (UBA), and a C-terminal kinase-associated domain (KA1). The last 15 residues closely match a conserved nuclear export sequence (NES) (Kazgan et al., 2010). Its sequence in Arabidopsis (AKIN10/11/12), yeast (SNF1), and human (AMPKα1/2) proteins is shown, with conserved bulky hydrophobic amino acids (L, I, F, V, and M) indicated in red, and the predicted amphipathic α-helical region underlined in AKIN10. The overall map is based on splice form At3g01090.2, which includes an additional 5′ exon. The first methionine of the product of two other splice variants, At3g01090.1 and At3g01090.3, is indicated (M24). The extent of two truncated cDNA clones from a cDNA library that interacted with PTL in yeast cells is shown. Blue bars indicate the regions of AKIN10 and PTL required for their interaction.