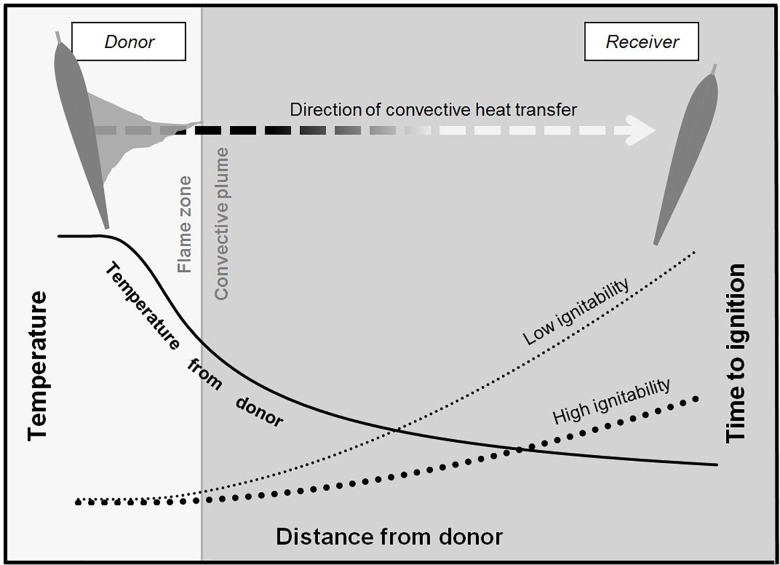
Fig 1. Ignition of a receiver leaf by a burning donor.
The flame from the donor produces a convective plume following a direction described by the flame angle (broken arrow), where the temperature of the air in the plume decreases with distance from the donor (solid curve) in a pattern determined by the flame produced from that leaf. The time of heating required for ignition of the receiver increases as the temperature decreases, at a rate determined by the ignitability of the leaf. The plume temperature model is taken from [37], and the time to ignition modelled from [35], where ignitability is a function of plume temperature and the Ignitability Coefficient (IC = leaf moisture (% Oven Dry Weight) * thickness (mm) / number of sides on the leaf).