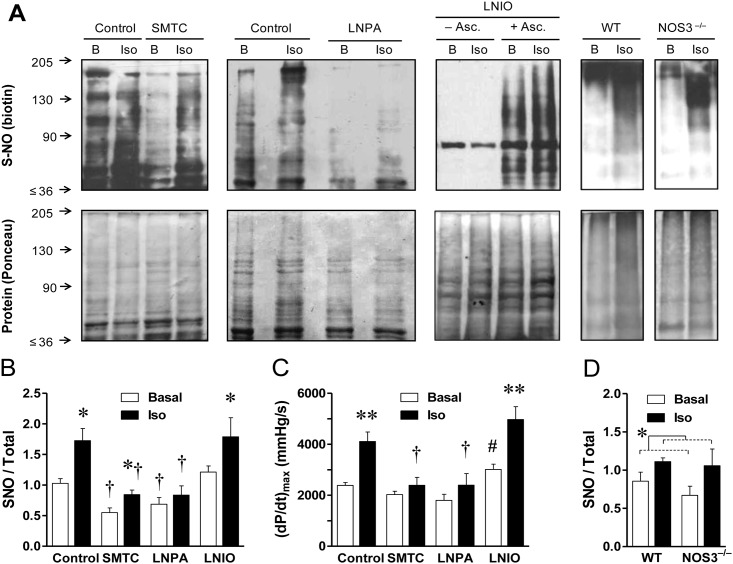
Fig 3. Inhibition of NOS-1 reduces basal level of protein S-nitrosylation in the heart and isoproterenol causes rapid NOS-1-dependent protein S-nitrosylation.
(A) Representative Western blots showing protein S-nitrosylation in hearts homogenized during baseline (B), or after stimulation with isoproterenol (10nM, 3-min, Iso); in control conditions, or after 20-min treatment with NOS-1 inhibitor, L-Methyl-thio-citrulline 300nM (SMTC), or Nω—propyl—L—arginine 200nM (LNPA), or NOS-3 inhibitor L-N5-(1-Iminoethyl)ornithine 1μM (LNIO). Homogenized tissue was submitted to the biotin-switch procedure, followed by SDS-PAGE analysis. The same membranes are shown stained for biotin (top) and for total protein content (Ponceau red, bottom). A representative control for the specificity of the biotinylation reaction, is shown in the LNIO panel, where same pair of samples was incubated without ascorbate (–Asc.) or with this reducing agent (+ Asc.). The far right panels show S-nitrosylation analysis of hearts obtained from wild type (WT) and NOS-3 deficient (NOS3–/–) mice. (B) Densitometric analysis of normalized biotin/Ponceau signal for the series of rat hearts (Control n = 8, SMTC n = 8; LNPA n = 5, LNIO n = 6). All proteins included in the rectangular area (range ~35–210 KDa) were quantified. Two-way ANOVA indicated significant effect of inhibitors (p<0.005) and β-adrenergic stimulation (p<0.0005), without significant interaction. Asterisk indicates p<0.05 Iso vs. respective Basal; † indicates p<0.01 vs. corresponding Control and LNIO value. (C) Cardiac contractility determined in the same rat hearts immediately prior to homogenization. Two-way ANOVA indicates significant effect of inhibitors (p<0.005), isoproterenol (p<0.01), and interaction (p<0.05). ** p<0.01 Iso vs. respective Basal; † indicates p<0.01 vs. corresponding Control value; # p<0.05 LNIO vs. all other basal values. (D) Densitometric analysis of normalized biotin/Ponceau signal for the experimental series of WT and NOS-3–/–mice hearts. According to two-way ANOVA there was significant effect of Isoproterenol (*, p<0.05), but no significant effect of strain or interaction (n = 3 per group).