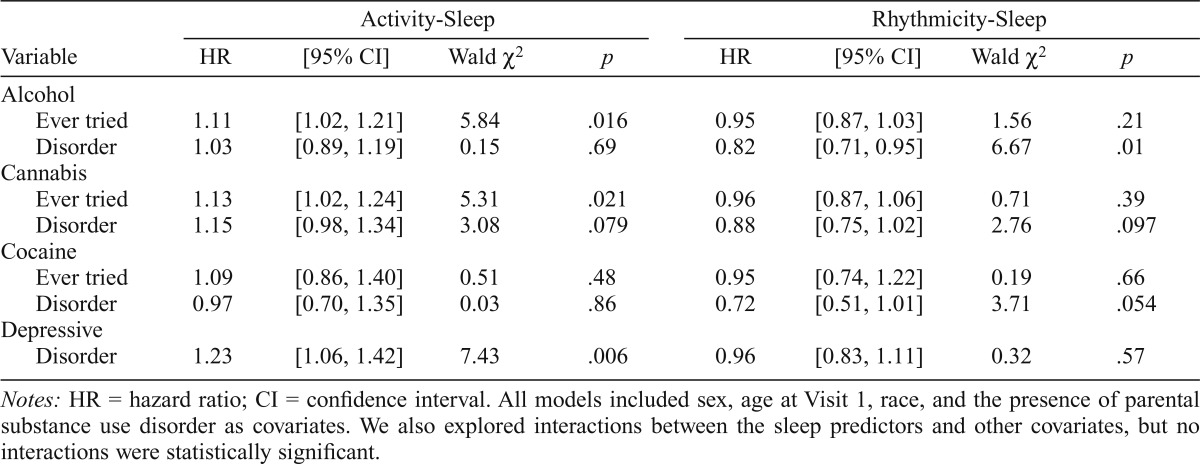
Table 1.
Results from Cox proportional hazards models
| Activity-Sleep |
Rhythmicity-Sleep |
|||||||
| Variable | HR | [95% CI] | Wald χ2 | P | HR | [95% CI] | Wald χ2 | P |
| Alcohol | ||||||||
| Ever tried | 1.11 | [1.02, 1.21] | 5.84 | .016 | 0.95 | [0.87, 1.03] | 1.56 | .21 |
| Disorder | 1.03 | [0.89, 1.19] | 0.15 | .69 | 0.82 | [0.71, 0.95] | 6.67 | .01 |
| Cannabis | ||||||||
| Ever tried | 1.13 | [1.02, 1.24] | 5.31 | .021 | 0.96 | [0.87, 1.06] | 0.71 | .39 |
| Disorder | 1.15 | [0.98, 1.34] | 3.08 | .079 | 0.88 | [0.75, 1.02] | 2.76 | .097 |
| Cocaine | ||||||||
| Ever tried | 1.09 | [0.86, 1.40] | 0.51 | .48 | 0.95 | [0.74, 1.22] | 0.19 | .66 |
| Disorder | 0.97 | [0.70, 1.35] | 0.03 | .86 | 0.72 | [0.51, 1.01] | 3.71 | .054 |
| Depressive | ||||||||
| Disorder | 1 .23 | [1.06, 1.42] | 7.43 | .006 | 0.96 | [0.83, 1.11] | 0.32 | .57 |
Notes: HR = hazard ratio; CI = confidence interval. All models included sex, age at Visit 1, race, and the presence of parental substance use disorder as covariates. We also explored interactions between the sleep predictors and other covariates, but no interactions were statistically significant.