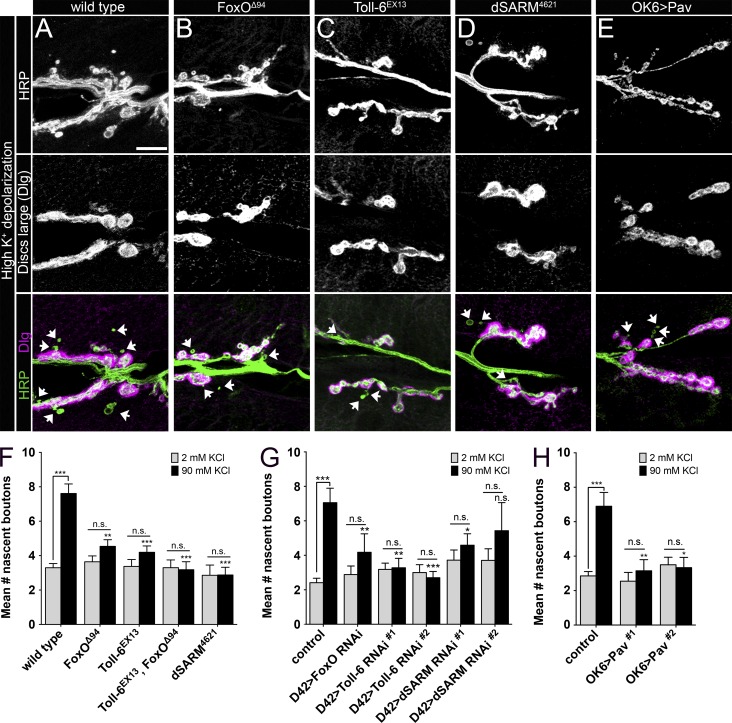
Figure 5.
Toll-6, dSARM, and FoxO are required for rapid presynaptic structural plasticity. (A–E) Representative confocal projections of NMJ6/7 in A2-3 labeled with HRP and Dlg after high K+ stimulation. Arrows denote nascent boutons. Bar, 10 µm. (F) Quantification of nascent boutons after high K+ and control stimulation paradigms. Wild type2mM: 3.3 ± 0.2 (n = 27); wild type90mM: 7.6 ± 0.6 (n = 31); foxOΔ942mM: 3.6 ± 0.3 (n = 14); foxOΔ9490mM: 4.5 ± 0.4 (n = 26); Toll-6EX132mM: 3.4 ± 0.4 (n = 16); Toll-6EX1390mM: 4.2 ± 0.4 (n = 31); Toll-6EX13, foxOΔ942mM: 3.2 ± 0.5 (n = 10); Toll-6EX13, foxOΔ9490mM: 3.2 ± 0.5 (n = 11); dSARM46212mM: 2.9 ± 0.6 (n = 7); and dSARM462190mM: 2.9 ± 0.5 (n = 16). Wild type is OregonR. (G) Quantification of nascent boutons after high K+ and control stimulation paradigms. Control2mM: 2.4 ± 0.3 (n = 17); control90mM: 7.1 ± 0.8 (n = 18); D42>dcr-2; foxO RNAi2mM: 2.9 ± 0.5 (n = 17); D42>dcr-2; foxO RNAi90mM: 4.2 ± 1.1 (n = 17); D42>dcr-2; Toll-6 RNAi#12mM: 3.2 ± 0.4 (n = 22); D42>dcr-2; Toll-6 RNAi#190mM: 3.3 ± 0.5 (n = 18); D42>dcr-2; Toll-6 RNAi#22mM: 3.0 ± 0.5 (n = 15); D42>dcr-2; Toll-6 RNAi#290mM: 2.7 ± 0.4 (n = 20); D42>dcr-2; dSARM RNAi#12mM: 3.7 ± 0.6 (n = 25); D42>dcr-2; dSARM RNAi#190mM: 4.6 ± 0.7 (n = 29); D42>dcr-2; dSARM RNAi#22mM: 3.7 ± 0.7 (n = 17); and D42>dcr-2; dSARM RNAi#290mM: 5.4 ± 1.6 (n = 14). Control is D42>dcr-2. (H) Quantification of nascent boutons after high K+ and control stimulation paradigms. Control2mM: 2.9 ± 0.3 (n = 27); control90mM: 6.9 ± 0.8 (n = 29); OK6>Pav#12mM: 2.5 ± 0.5 (n = 11); OK6>Pav#190mM: 3.2 ± 0.6 (n = 20); OK6>Pav#22mM: 3.5 ± 0.4 (n = 17); and OK6>Pav#290mM: 3.3 ± 0.6 (n = 12). Control is OK6Gal4/+. Error bars are mean ± SEM. n.s., not significantly different. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Statistical comparisons above 90 mM bars are to 90 mM measurements of wild type or control.