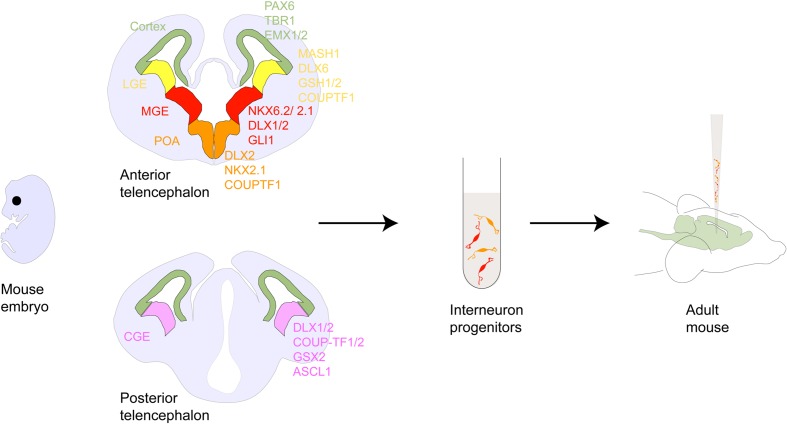
FIGURE 1.
Interneuron development within the forebrain. Schematic showing coronal sections of the rodent anterior and posterior telencephalon. Shown are the pallial and subpallial neurogeneic niches and their gene expression patterns. Following the discovery of tangentially migrating neurons in the developing cortex (Walsh and Cepko, 1988, 1993) several cell lineage studies demonstrated that many of these neurons originated in the ventral telencephalic ganglionic eminences and the POA and ultimately matured into GABAergic interneurons. For example, ablation of the embryonic ventral telecephalon or mutation of the homeodomain transcription factor gene Dlx1/2 heavily expressed in this region results in a dramatic loss of neocortical GABAergic neuron populations (Anderson et al., 1997). Ventral fate inducing sonic hedgehog(SHH) signaling has been shown to specify PV and SST expressing interneuron differentiation from ventral telencephalic progenitors in culture and in vivo (Xu et al., 2010; Tyson et al., 2015). Several other homeobox genes such as Mash1 (Casarosa et al., 1999), Nkx2.1 (Sussel et al., 1999), Lhx6 (Liodis et al., 2007), and FGFR (Gutin et al., 2006), as well as guidance cues such as the chemorepulsive semaphorin/neuropilin (Marín et al., 2001) and chemoattractive neuregulin-1/ErbB4 (Flames et al., 2004) interactions have been shown to be critical for proper direction and selection of GABAergic cell identity, subtype and migration. Genetic fate mapping of transplanted embryonic cells in cultures or in utero has revealed that MGE gives rise to PV- and SST-, while CGE gives rise to CR-, VIP- and Reelin-expressing interneurons, with each cell group having a distinct spatio-temporal origin (Nery et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2004; Butt et al., 2005; Miyoshi et al., 2010; Petros et al., 2015). In addition, the POA has been shown to be the origin of at least 10 percent of GABAergic interneurons comprising of PV-, SST- and a small percentage of VIP-, NOS-, and CR-expressing interneurons (Gelman et al., 2011). Abbreviations: LGE, MGE, CGE (lateral, medial, caudal ganglionic eminence); POA (preoptic area); CB (cabindin), CR (calretinin), PV (parvalbumin), SST (somatostatin), NPY (neuropeptide Y), RLN (reelin), NOS (nitrous oxide) expressing interneurons.