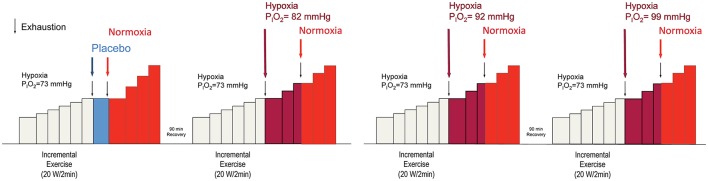
Figure 1.
Experimental protocol. Each experimental day the subjects performed two incremental exercise tests in random order. The incremental exercise test always began in severe hypoxia (PIO2 = 73 mmHg). At exhaustion (Exh1) the breathing gas mixture was swiftly changed to another one with a greater oxygen PO2, except in one instance that the gas administered was the same one the subjects were breathing in severe acute hypoxia, i.e., PIO2 = 73 mmHg, to create a placebo condition. Subjects were asked to continue the exercise and after 2 min at the load eliciting Exh1, the load was increased by 20 or 30 W/2 min until exhaustion (Exh2). Once again, subjects were asked to keep pedaling while the gas mixture was swiftly changed to normoxia. After 2 min at the load eliciting Exh2, the intensity was increased by 20 or 30 W/2 min until the final exhaustion (Exh 3). Between Exh1 and Exh2, the breathing gas mixtures used corresponded to PIO2 of 73, 82, 92, 99, and 142 mmHg (Normoxia) and were administered following a double-blind design. Subjects were asked to pedal close to 80 rpm. However, when approaching exhaustion, the pedaling rate was always reduced.