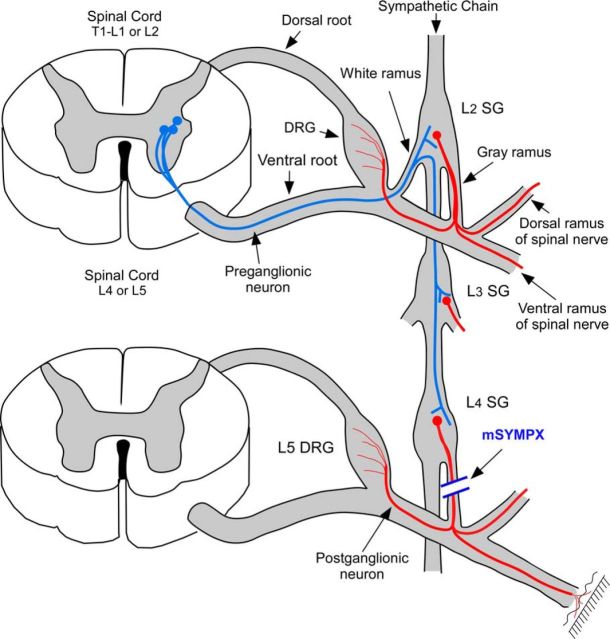
Figure 1.
Diagram of mSYMPX procedure. Red represents postganglionic sympathetic cells in the paravertebral ganglia. They are innervated by preganglionic neurons (blue) in the intermediolateral column of the thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord, with axons entering via the white rami, which may then travel through several levels of the paravertebral chain before synapsing on the postganglionic neurons. There are no white rami at the L4/L5 level. A few postganglionic neurons at this level send axons through the gray rami to reach the blood vessels and surface of the adjacent DRG, whereas most travel in the dorsal or ventral rami of the L4 and L5 spinal nerves to peripheral targets. For simplicity, these 3 possible projection pathways are shown as single postganglionic neuron; this is not meant to imply that any one neuron projects in all three pathways. Some postganglionic axons in the L4 or L5 gray rami originate from cell bodies of more rostral sympathetic ganglia whose axons travel through the chain for a few levels before entering the gray rami (not shown). Diagram is not to scale. mSYMPX was performed by cutting the gray rami to the L4 and L5 spinal nerves on one side.