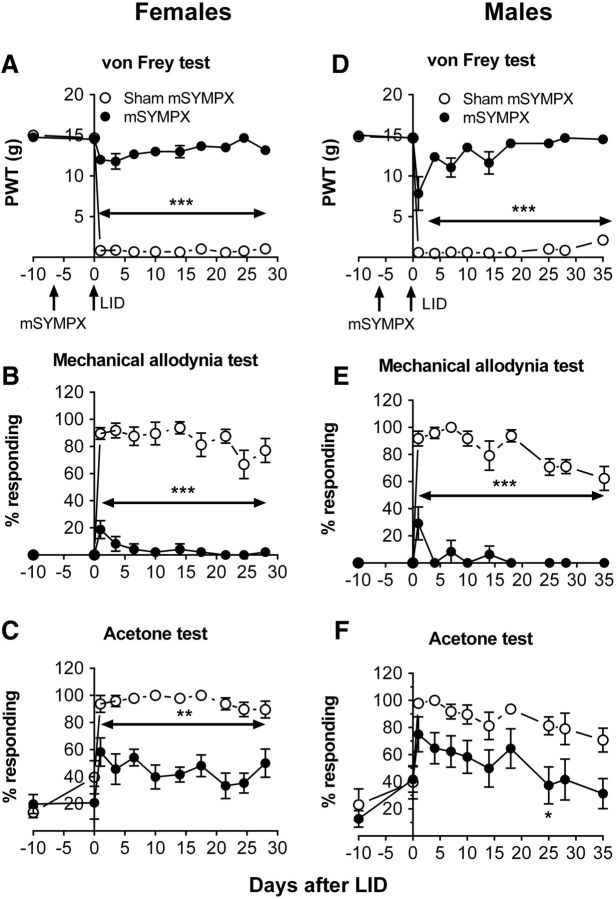
Figure 2.
Effect of prior mSYMPX on pain behaviors induced by local DRG inflammation is similar in both sexes. Behaviors were measured before any surgery, and the average baseline is plotted on POD −10. A first surgery was performed to cut the gray rami to the ipsilateral L4 and L5 (mSYMPX) or the corresponding sham surgery. Behavior was measured again 3–10 d later; no effects of mSYMPX or sham mSYMPX on baseline behaviors were observed (data plotted on day 0). After this behavior measurement, on POD 0, a second surgery was performed to locally inflame the L5 DRG (LID). A, D, Paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) to von Frey stimuli was reduced by LID but remained near baseline in LID + mSYMPX animals. B, E, Mechanical allodynia(withdrawal response to light stroking with a cotton wisp) was significantly increased by LID but largely absent in the mSYMPX group. C, F, Cold allodynia (withdrawal responses to a drop of acetone on the paw) was increased by LID and significantly reduced by mSYMPX on the indicated days. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, significant difference between LID + sham mSYMPX and LID + mSYMPX groups at indicated time points (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Left, Female rats, N = 8 per group; experimenter was blinded as to the sham/mSYMPX status. Right, Male rats, N = 8 per group.