Fig. 7. PfEMP1 surface-exposure and cytoadherence of REX1 transfectants.
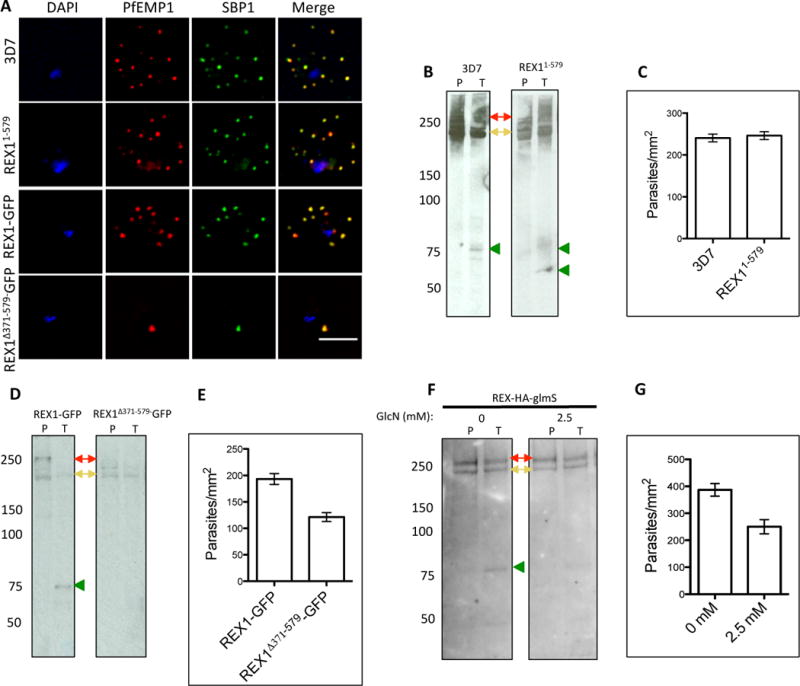
A. Immunofluorescence microscopy of acetone-fixed RBCs infected with 3D7 and REX1 transfectants. Maurer’s clefts were identified by immunolabeling with anti-SBP1 (green). Anti-PfEMP1 antibodies (red) revealed colocation of the virulence protein with Maurer’s clefts. The nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 3 μm. B, D, F. Trypsin digestion of surface-exposed PfEMP1 in RBC infected with wildtype and REX11–579 transfectants (B), in REX1-GFP and REX1(Δ371–579)-GFP transfectants (D) and in REX1-HA-GlmS parasites without or with treatment with 2.5 mM GlcN. Full-length PfEMP1 (~270 kDa, red arrows) and a cross-reactive spectrin band (~240 kDa, yellow arrows) are indicated. Trypsin cleavage products (75 kDa) are indicated with green arrowheads. The data are representative of three separate experiments. C, E, G. Adherence of trophozoite-stage infected RBCs to recombinant CD36 under flow conditions (0.1 Pa) ± S.E.M. measured in 10 different areas in each of three separate experiments. REX1(Δ371–579)-GFP binding was significantly lower than REX1-GFP (p < 0.0001, unpaired t-test).
