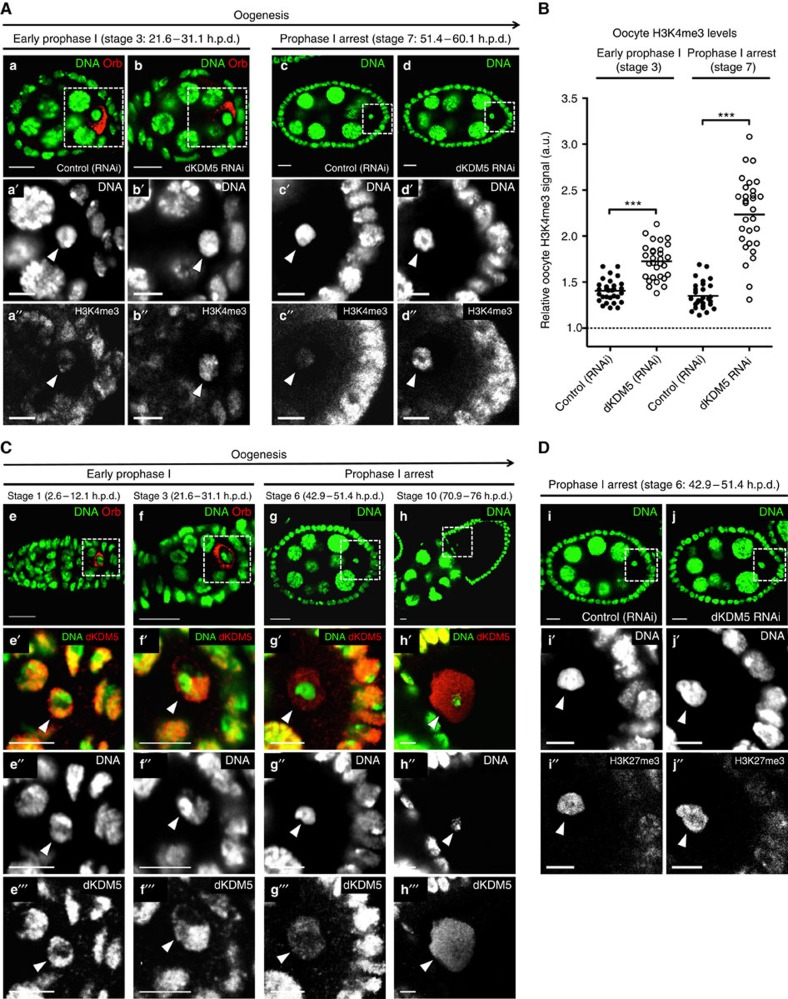
Figure 3. Oocyte H3K4me3 levels are specified in early oogenesis by the histone demethylase dKDM5.
(A,B) Germ line-specific knockdown of the histone demethylase dKDM5 significantly increases histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) levels in prophase I oocytes (a–d′′). Oocyte H3K4me3 levels were compared at stages 3 and 7 of oogenesis (before and after the establishment of the prophase I arrest, respectively). Signal quantification (B) is represented per oocyte and is expressed in fluorescence arbitrary units (a.u.). Horizontal lines specify mean values and asterisks indicate significant difference (Mann–Whitney U-test; P<0.0001). Similar results were obtained with a dkdm5−/− mutant (Supplementary Fig. 4A,B). (C) dKDM5 is evicted from oocyte chromatin during early oogenesis, prior to the establishment of the prophase I arrest (e–h′′′) At the very start of prophase I (oogenesis stage 1), dKDM5 co-localizes with oocyte chromatin (e–e′′′) As the oocyte's chromosomes begin to cluster together to form the karyosome (oogenesis stage 3), dKDM5 is partially evicted from chromatin (f–f′′′) During the prophase I arrest (oogenesis stage 6 as representative example) dKDM5 does not co-localize with oocyte chromatin, being restricted to the nucleoplasm (g–g′′′) dKDM5 remains evicted during the transcriptional reactivation of the oocyte in late prophase I (oogenesis stage 10; h–h′′′). See Supplementary Fig. 9 for quantification. The dKDM5 signal corresponds to a genomic dkdm5 transgene containing a C-terminal human influenza hemagglutinin (HA) tag crossed into the dkdm5−/− mutant background (antibody: anti-HA). (D) Oocyte heterochromatin is not globally affected by the germ line-specific knockdown of dKDM5. Heterochromatin of both the facultative (histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation—H3K27me3) and constitutive (histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation—H3K9me2) type remained unchanged after dKDM5 knockdown (i–j′′ and Supplementary Fig. 6). Quantifications of oocyte H3K27me3 and H3K9me2 levels are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6. (A–D) Development time in relation to the start of oogenesis is expressed in hours post-germ line stem cell division (h.p.d.). Rectangles delimit the area of the oocyte insets and arrowheads point to the oocyte chromatin/nucleus. To distinguish early prophase I oocytes from other germ line cells, an oocyte cytoplasm-specific staining was performed (Orb). Scale bars, 10 μm for ovarian follicles and 5 μm for oocyte insets.