Figure 1. Transcriptomics profile of the perilesional cortex, ipsilateral thalamus, and ipsilateral hippocampus at 3 months after lateral fluid-percussion-induced traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rat.
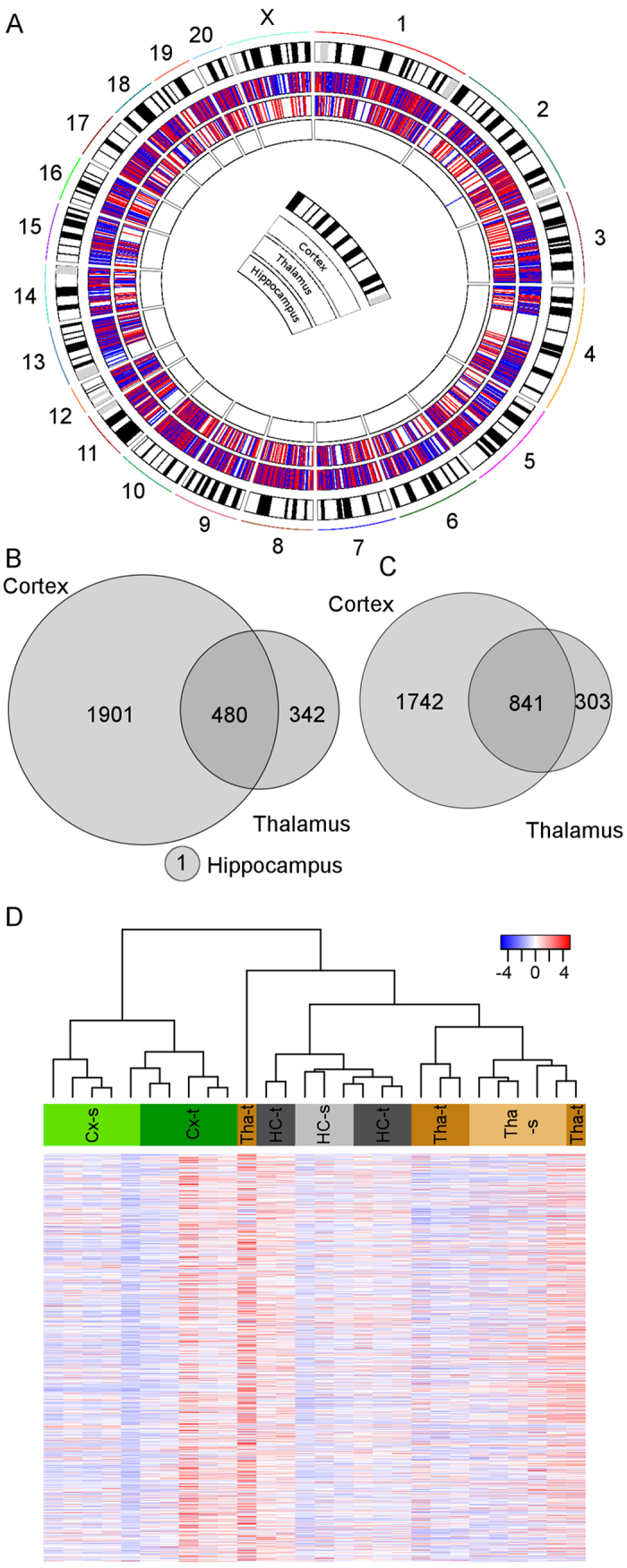
(A) A circos plot showing the chromosomal location of differentially expressed genes in the cortex (outermost circle), thalamus (middle), and hippocampus (innermost). We found 4964 differentially expressed genes in the cortex, 1966 in the thalamus, and only 1 in the hippocampus. Red lines indicate upregulated and blue lines downregulated genes. (B) Venn-diagram showing the number of common downregulated genes in the perilesional cortex, thalamus, and hippocampus. Altogether, 480 genes were downregulated in both the perilesional cortex and ipsilateral thalamus. (C) Venn-diagram showing the number of common upregulated genes. Altogether, 841 genes were upregulated in both the perilesional cortex and ipsilateral thalamus. Note the absence of any upregulated genes in the ipsilateral hippocampus. (D) Hierarchically clustered heatmap of differentially expressed genes in the perilesional cortex, thalamus, and hippocampus. Sham-operated and injured animals clustered into their own clusters. Also, the perilesional cortex, thalamus, and hippocampus clustered into their own clusters. Thalamic expression in one rat with TBI, however, clustered into its own branch. Abbreviations: Cx-s, cortex sham-operated animal; Cx-t, cortex TBI; HC-s, hippocampus sham-operated animals; HC-t, hippocampus TBI; Tha-s, thalamus sham-operated animal; Tha-t, thalamus TBI.
