Figure 3. Simultaneous multiple splitting.
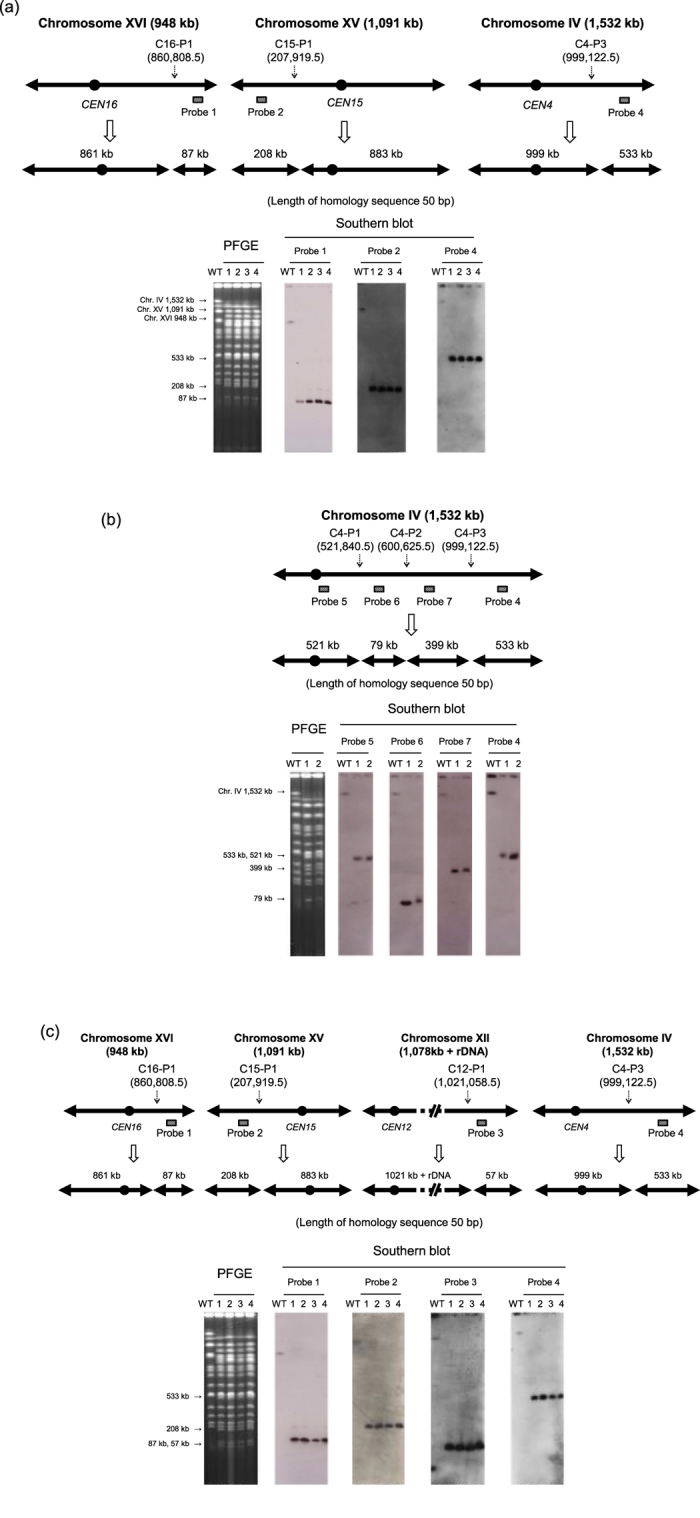
(a) Simultaneous triple splitting by CRISPR-PCS. Three sites (C16-P1, C15-P1, and C4-P3) were targeted. A 50 bp homology sequence was used in the splitting module. The splitting modules of C16-P1, C15-P1, and C4-P3 were marked with CgLEU2, CgHIS3, and URA3, respectively. Wild type FY834-Cas9 and four randomly chosen transformants were subjected to PFGE and subsequent Southern blot analysis. Probes 1, 2, and 4 were used to detect Chr. XVI, Chr. XV, and Chr. IV respectively. (b) One step construction of four chromosomes from one chromosome. Chr. IV was targeted to split at three positions (C4-P1, C4-P2, and C4-P3). A 50 bp homology sequence was used in the splitting module. The splitting modules of C4-P1, C4-P2, and C4-P3 were marked with CgHIS3, CgLEU2, and URA3, respectively. Wild type FY834-Cas9 and two randomly chosen transformants were subjected to PFGE and subsequent Southern blot analysis. Probes 5, 6, 7, and 4 were used to detect the 522 kb, 79 kb, 398 kb, and 533 kb chromosomes, respectively. (c) Simultaneous quadruple splitting by CRISPR-PCS. Four sites (C16-P1, C15-P1, C12-P1, and C4-P3) were targeted. A 50 kb homology sequence was used in the splitting module. The splitting modules of C16-P1, C15-P1, C12-P1, and C4-P3 were marked with CgLEU2, CgHIS3, KanMX, and URA3, respectively. Wild type FY834-Cas9 and four randomly chosen transformants were subjected to PFGE and subsequent Southern blot analysis. Probes 1, 2, 3, and 4 were used to detect Chr. XVI, XV, XII, and IV, respectively.
