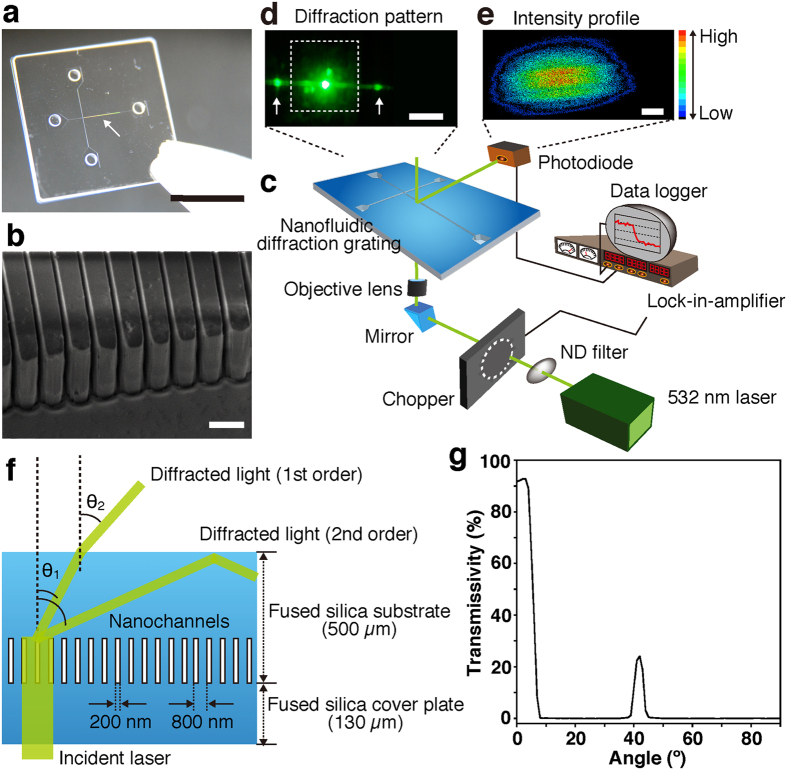
Figure 1. Label-free detection system using the nanofluidic diffraction grating.
(a) A photo of the nanofluidic diffraction grating; scale bar, 1 cm. Interference fringes indicated the nanochannels were embedded in the microchannel as marked by the white arrow. (b) A SEM image of the nanochannels, which was 800 nm period, and 200 nm width and 2.7 μm depth fused silica nanogrooves; scale bar, 1 μm. (c) A schematic illustration showing the setup for label-free detection using signal changes of the diffracted light when the nanofluidic diffraction grating was filled with a sample (various liquids, DNA molecules, or amplified DNA molecules). (d) A photo showing the diffracted light (white arrows) and the origin of the beam; scale bar, 1 cm. The white dotted lines outline the nanofluidic diffraction grating. (e) A two-dimensional (2D) intensity profile of the diffracted light; scale bar, 1 mm. Color gradation showing intensity variation; red and black colors mean high and low intensities, respectively. (f) A schematic illustration showing the diffraction of light through the device. (g) Transmissivity for the wavelength of 532 nm at each output angle. The 532 nm laser beam has some transmittance at 42°.